The battery, as the name implies, is a device for storing electrical energy. At the right time, this energy lights up LEDs or incandescent bulbs in the lanterns, drives electric motors, powers electronic devices, and provides uninterruptible power supply units.
Parallel and serial, as well as combined battery connections are used to assemble batteries with different characteristics.

Types of products for various purposes
Why connect power sources
Combining separate power sources, you can get several benefits:
- Raise the supply voltage.
- Reduce or increase the current in the consumer circuit.
- Increase overall battery assembly capacity.
Power consumption is equal to the product of the voltage applied to the consumer and flowing in the current circuit.
Thus, by increasing the supply voltage, it is possible to reduce the load on the wires from the flowing current. It is easy to see that the larger the current parameter, the more conductors are heated. Heating does not produce any work, which means that the total efficiency of the electrical device is reduced.
Important! By increasing the supply voltage, and reducing the flowing current, energy is saved by reducing heat losses in the circuit.
Key Features of rechargeable batteries
Before starting the “experiments” and connecting the batteries, you need to understand what characteristics they have and what each type of connection gives.
The first characteristic is the rated voltage. The parameter determines what voltage can be between the positive and negative terminals. This characteristic is not constant and the nominal value is issued to the circuit only from a fully charged power source, as the discharge and under load, the electromotive force (EMF) decreases.
Today, the most popular values are 1.2, 2.4, 6 or 12 Volts.
Note! The minimum voltage of the drives is 1.2 Volts, and not 1.5 V as with “disposable” batteries.
By connecting several sources in series, they achieve increased voltage at the output of the assembly.
The capacity indicates how much electricity the device is capable of delivering before reaching the minimum acceptable discharge level and is measured in amperes / hours.
For example, the designation 50 A / h means that at a current equal to 1A, the battery will provide power for 50 hours, or at a current of 2 A it will work 25 hours until the next charge.
The presented calculation is approximate and is valid only for low discharge currents. High current discharges the battery faster. You can clarify the characteristic according to the discharge characteristics diagrams attached to the products.
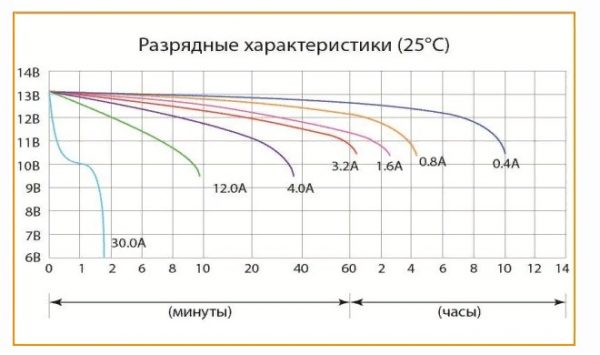
An example of a discharge characteristic depending on the load current
The total capacity for any type of connection will be equal to the total indicators of all the batteries included in the circuit.
Serial connection
The serial connection scheme involves the conductor connecting the positive pole of the first source and the negative second. Next, the positive output of the second power source is connected to the negative of the third and so on. The assembly terminals are the negative terminal of the first battery and the positive terminal in the circuit.
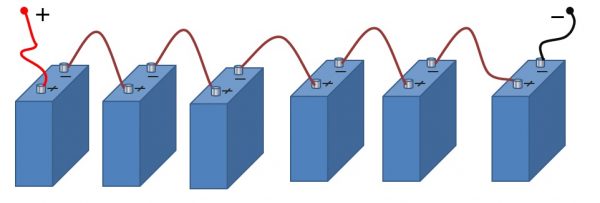
Serial connection
The total voltage of such an assembly will be equal to the sum of the EMF of all sources included in the network. If drives of the same capacity are included in the battery, then the total value will remain equal to the characteristic of one source.
For example, when 3 products are connected in series at 1.2 V each, the total voltage between the output terminals of the first and third connected sources will be 3.6 V.
When an electric current is connected to the receiver circuit, a current will flow through the serial circuit, not exceeding the capacity of 1 source of electricity. For example, if the assembly is made of the same 2000 mAh batteries, then the total value for any number of “cells” in the circuit will remain at the same value.
The meaning of the serial connection is to increase the voltage in the network, and at low currents provide increased output at the output.
Features of sequential inclusion
When sequentially turned on, they strictly observe the rules, the failure of which leads to a quick battery failure, and in some cases is dangerous to the user's health.
Each power supply has internal resistance. For products made according to the same technology, using the same components and having the same characteristics, the internal resistance is approximately the same and depends mainly on the degree of charge.
The same in manufacture, but different in capacity batteries, internal resistance is very different. The same applies to batteries with different manufacturing techniques.
What is the danger of connecting power supplies with different characteristics when charging and discharging series-connected products.
Charging
When you turn on the series-connected batteries of different capacities, each of them will be charged with one current, which gives the charger. With a difference in capacity by half, the smaller of the drives will charge about three times faster than large ones.
Thus, after some time, some of the batteries will gain a full charge, while large batteries will need further supply of charging current.
Two outcomes are possible:
- Unloading of "large" sources if the charger is turned off. Consequently, in the future, connected consumers will not work for a long time.
- Recharging a smaller battery if the charge is not disconnected. As a result, overheating. Boiling electrolyte, failure of the product. Explosion is possible.
Attention! Charging sequentially connected drives is allowed only if they have the same capacity and voltage.
Discharge
The discharge process is no less dangerous for different sources. The current at each point in the series circuit is the same. A battery of a smaller capacity will discharge faster than more powerful devices connected in series with it. If the circuit has a device for protection against deep discharge, then the consumer's power will stop when powerful batteries are still able to give current. The effectiveness of the general assembly will be reduced several times.
If the device is not equipped with protection, then the current flow will continue. As a result of a deep discharge, the smallest device will inevitably fail.
Parallel connection
With a parallel connection, all the advantages of power supplies must be connected to one point. Do the same with the negative poles.
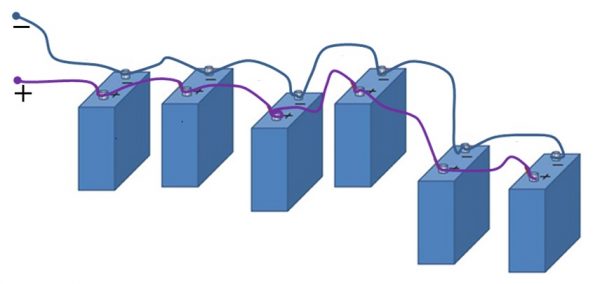
Parallel connection
When connecting this type, other rules for determining assembly characteristics apply.
It is allowed to use a parallel connection for batteries of different capacities, provided that the rated voltage of the products is the same.
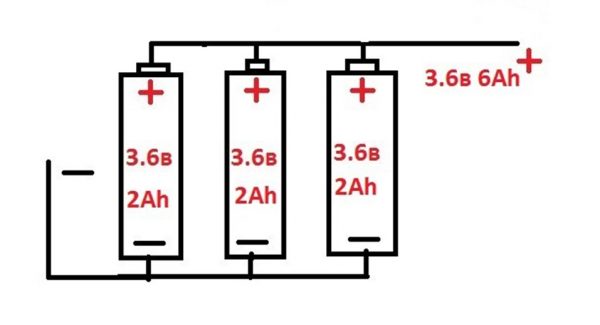
Example of changing characteristics in parallel
The total capacity of the parallel assembly will be equal to the sum of the capacities of all included products. By connecting two identical batteries in parallel, they get an assembly of twice the capacity. Each of the sources is discharged and charged with an acceptable current for it.Small discrepancies in the initial stages of the cycles do not have a significant impact on the time of good operation.
At the first connection, it is important that the degree of charge and, accordingly, the voltage at the terminals of the connected products is equal.
This is caused by the fact that if a smaller battery is charged more (higher output voltage), then a larger battery will become a consumer of electricity (a small battery will start to “charge” a larger one). This is fraught with overcurrent and destruction. The same effect will be observed if the voltage is higher on a battery with a larger capacity. In this case, a source with a lower voltage level will become a load, a current close in value to a short circuit will flow through it.
Attention! It is forbidden to connect batteries with different rated voltages in parallel.
In addition to the failure of large drives, a large current will flow between the terminals and connecting wires at the time of connection. This in turn can lead to damage or even destruction. Sparking between two sources with different voltages is a source of ultraviolet radiation, which is dangerous for human vision.
Connect the batteries in a parallel circuit only after preliminary alignment of the EMF.
Parallel serial connection
In parallel, a consistent method of connecting batteries is often used to create power supplies for various portable power tools. The method allows you to get a "high" voltage with a large capacity.
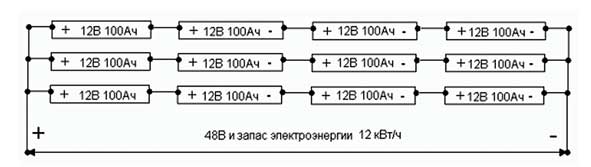
Parallel to serial connection
Several products are connected in series, obtaining the desired voltage. Then these chains are connected in parallel, winning in the capacity of the general assembly.
The connection rules apply the same as for the previously described inclusion methods. In such devices, it is customary to connect batteries with the same characteristics. Applying “batteries” from one batch, approximately the same internal resistance of the components is obtained.
Different switching schemes are needed to ensure the operation of various devices requiring autonomous power. Applying the knowledge gained in the article, you can make independent connections necessary for the correct operation of the equipment.
 Replacing the battery in ipad mini
Replacing the battery in ipad mini  18650 batteries: description, specifications and selection
18650 batteries: description, specifications and selection  Ni mh batteries: device, charging, model selection
Ni mh batteries: device, charging, model selection  DIY battery charger
DIY battery charger  Selection, device and charging of the gel battery, popular models
Selection, device and charging of the gel battery, popular models 

