Everyone who has dealt with rechargeable batteries knows that their main characteristics are rated voltage and charge capacity. But to maintain battery performance, an equally important parameter is battery density. Of course, in fact, we are talking about the density of the electrolyte in the battery. But often it is this slang expression that is used. Monitoring the electrolyte concentration is as necessary as regularly charging the current source.
What is affected by electrolyte density
Most batteries use lead plates, and the working medium is sulfuric acid diluted with water. The saturation of the solution, measured in grams / cm3, is the characteristic that affects the battery’s ability to accumulate charge for later use.
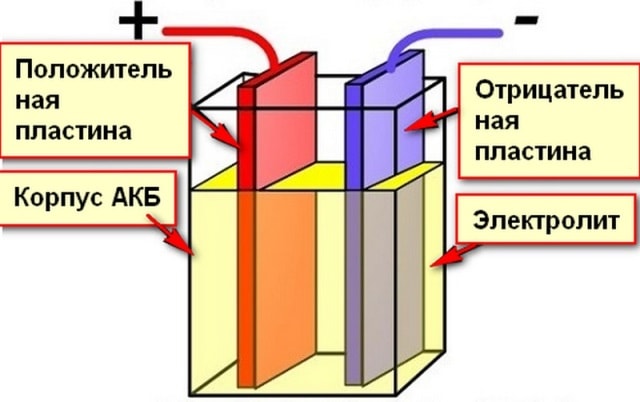
Lead Acid Battery Design
The concentration of acid in the electrolyte solution and the performance of the battery are directly related.
- At a low density, the ability of the current source to accumulate the charge capacity that ensures its performance also decreases. At a low density, the battery discharges faster and does not give out the set maximum current.
- If the value of this parameter drops below a certain value, then in frost the water in the electrolyte may freeze, and the battery will completely fail.
- But at high density, the process of sulfation of lead plates is sharply accelerated. This means that with a weak battery charge, lead sulfate is formed on them, which is no longer converted when it is charged back to lead. This also leads to a decrease in the ability to accumulate the necessary charge, and over time - to the complete failure of the battery.
Therefore, it is important to maintain the value of this parameter in accordance with established and tested standards. A significant reduction or excess of regulatory values does not contribute to the productive work of the battery.
Colds in which the contents of the battery may freeze are shown in the figure.
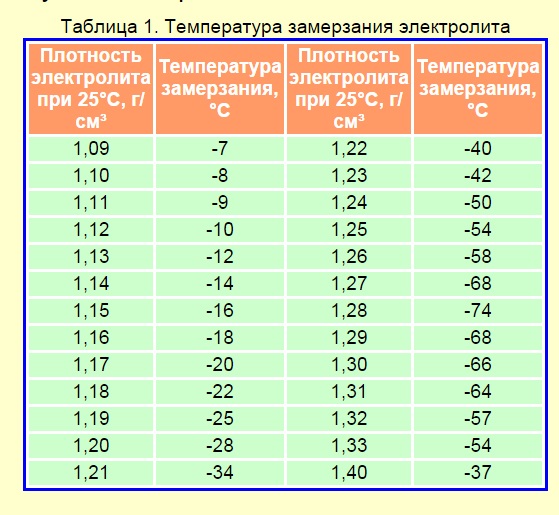
The freezing point of an aqueous acid solution, depending on its density
Normative electrolytic density indicators
Surely, many motorists familiar with the problems of maintaining battery performance know the figure of 1.27 g / cm3. Such is considered the optimal density at which acid batteries are able to maximize their capabilities.
But this value is not true for everyone. types of batteries and their work assignments. In addition, the optimal density varies for different temperatures at which the battery has to work. Therefore, the optimal values in winter and summer will be slightly different.
Purpose of lead-acid batteries
- Starter batteries are designed to provide the maximum possible current when starting various engines. This is, first of all, car batteries. The standard density value for them is 1.26 - 1.28 g / cm3.
- Traction batteries must provide DC electric motors for a long time. One of their applications is electric cars and other electric propulsion vehicles.The best value of the electrolyte density for these batteries is also in the range 1.26 - 1.28 g / cm3.
- Stationary batteries are used to power any electrical circuits and devices. Usually located in one place indoors. A reduced value of 1.22 - 1.24 g / cm3 is recommended for them.
Temperature dependent
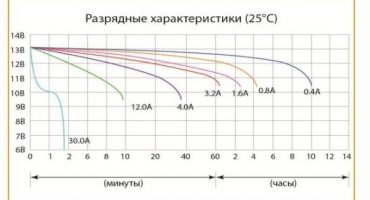
The surrounding temperature changes - the density values of the aqueous acid solution also change. With increasing temperature, the ability of the battery to accumulate charge increases by about 1% with each degree. With decreasing temperature, of course, this ability decreases. Therefore, it is recommended to keep the battery at high density values in cold weather, and to reduce these indicators for hot weather.
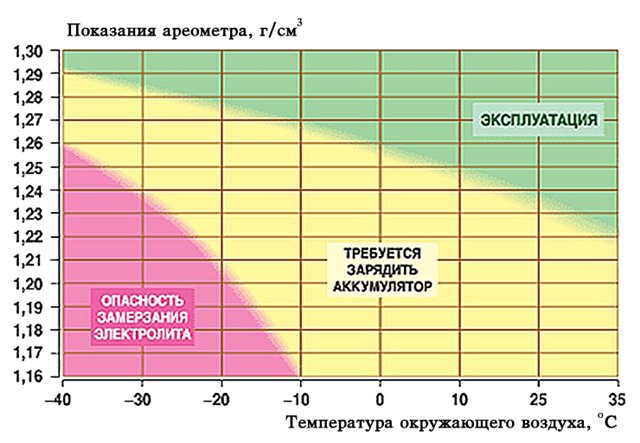
Battery performance at different temperatures depending on density
Of course, no one will deal with change at every jump in the weather. Just before the onset of cold weather it is useful to slightly increase the battery density, and before the summer season - lower it. In addition, there are norms of optimal density for areas with different climates. These normative values are supposed to be adhered to all year round, with rare exceptions. For different regions it is considered normal:
- In cold climates 1.27 - 1.30 g / cm3
- In the middle band 1.25 - 1.28 g / cm3
- In warm areas 1.22 - 1.25 g / cm3
In more detail these specifications are indicated in the table.
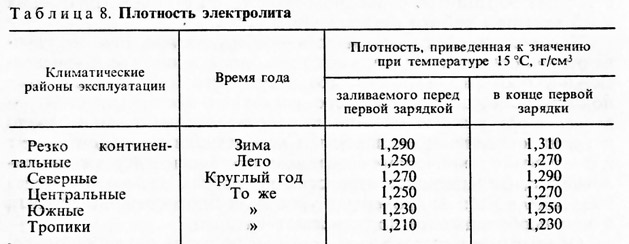
Standard values for battery electrolyte density for various temperature conditions
How to check electrolyte density in an acid battery
To test this characteristic, simple meters are available called automobile hydrometers or densimeters. Their work is based on the application of the Archimedes law, that is, the ability of the cargo to sink to different depths depending on the density of the liquid. Structurally, the hydrometer contains:
- Glass or plastic flask.
- Glass float with cargo and markings on it, corresponding to the measured values.
- A rubber bulb is worn on one side of the flask, designed to draw electrolyte into the flask.
- On the opposite side is a rubber nozzle through which liquid is taken from the filler hole of the battery.
The measured value is determined by the line on the float, which reaches the liquid collected in the hydrometer.

Single float car hydrometer
There are simpler hydrometers, in which there are several small stick weights with different weights for each. Each weight (or on the flask opposite it) has a corresponding density value. The measurement result is determined by the maximum value of the pop-up weights. Such a hydrometer is cheaper, but does not have sufficient accuracy.

Multi-float car hydrometer
The hydrometer measurement itself is carried out as follows:
- The hydrometer nose drops into the battery through the filler hole. There are devices not with rubber, but with a plastic nose. In this case, immerse it in the electrolyte carefully so as not to damage the lead plates.
- Using a pear, an electrolyte is collected in a flask. For hydrometers with a single float, you need to control the amount of fluid collected. It should be enough so that the float floats freely inside the bulb. But you can’t get a lot of fluid either. Then the float can rest against the upper edge of the bulb. The readings of the hydrometer in this case will be unreliable.
- After taking the liquid, we look - on the contrary, what are the risks on the float is its level. The numbers next to the risk will indicate the density value.
For hydrometers with several floats, the density value is determined by the floated floats. The floating weight with the maximum number on it just shows the measurement result.
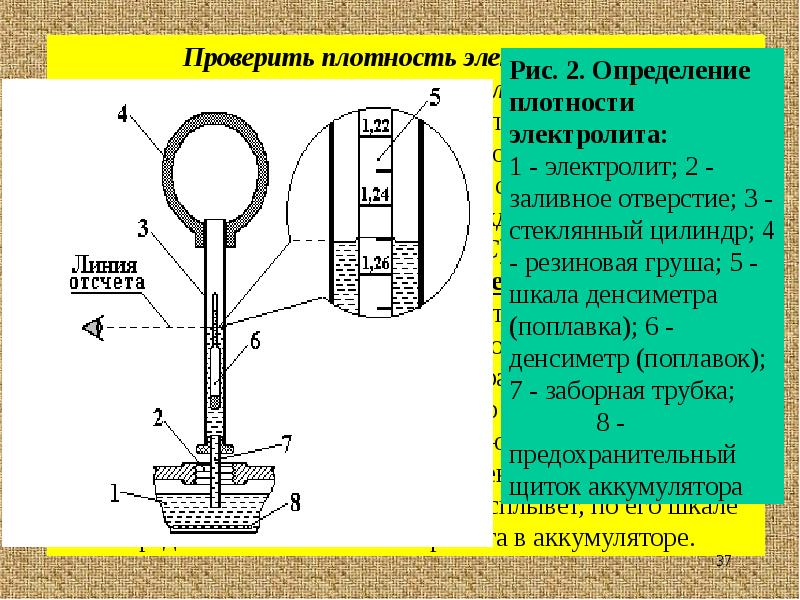
Reading using a hydrometer
For rechargeable batteries of several cells, verification is carried out separately in each bank.
The usual division price in battery hydrometers is 0.01 g / cm3. But hydrometers are also available with a more accurate scale.
After completing the measurements, the hydrometer should be thoroughly flushed with distilled water.
Conditions under which measurements should be made
Before starting measurements of the concentration of electrolyte, it is necessary to adhere to simple rules. And in some cases it will be necessary to correct the readings of the hydrometer depending on the conditions under which they were obtained.
The most necessary condition is to maintain the required fluid level in the battery itself. The density will be measured correctly, but for safe battery operation it will be necessary to bring the level to normal. And this will lead to a change in density.
Battery charge level
The density of the electrolyte changes when the battery is charged / discharged. When discharged, it decreases; when discharged, it increases. Depending on the degree of discharge of the battery, the values change as follows.
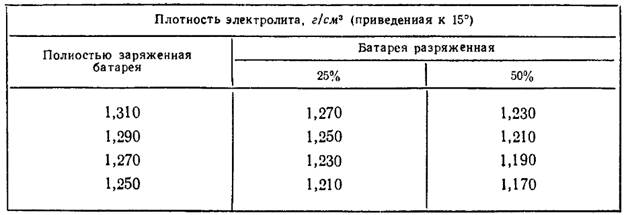
Dependence of hydrometer readings on the degree of battery charge
It is hardly possible to accurately determine the level of discharge. Therefore, you must first fully charge the battery, wait a few hours, and only then take measurements.
If any actions were carried out with a water-acid solution - by adding distilled water or the acid itself, then you should not measure the density immediately after them. It is necessary to wait until the topped up liquid is completely mixed in the battery.
Temperature during measurements
Calibration of standard hydrometers is oriented to a temperature of +25 ° С. To obtain the most accurate readings, electrolyte density should be measured at the same temperature. In winter, the tested battery should be brought to a warm place and allowed to warm up to the desired temperature. But you should not take measurements literally at home. An acid solution can accidentally spoil furniture or clothing. It is better to use a heated room adapted for such work.
If it is not possible to take measurements at a recommended temperature of 20 - 25 ° C, then you can take measurements at any temperature, and then use the correction table:
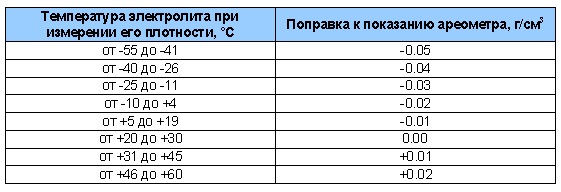
Correction values for measurements at different temperatures
Regular checks of the density of the electrolyte in the battery will allow not only to maintain it in optimal conditions for work, but also to identify possible problems and malfunctions in a timely manner.
 Replacing the battery in ipad mini
Replacing the battery in ipad mini  18650 batteries: description, specifications and selection
18650 batteries: description, specifications and selection  Ni mh batteries: device, charging, model selection
Ni mh batteries: device, charging, model selection  DIY battery charger
DIY battery charger  Selection, device and charging of the gel battery, popular models
Selection, device and charging of the gel battery, popular models