Induction cookers are gradually gaining popularity among housewives due to their cost-effectiveness. Is it really? Let’s try to figure out whether the induction cooker is really more economical than the electric one and how the power consumption of the induction cooker affects electricity bills.
How is the induction cooker and the principle of its operation
The induction hob consists of a housing, a temperature sensor, a control panel and a power unit.
The control panel controls the process. It is she who determines whether they put the dishes on her or not.
By the way, not all dishes are suitable for such a device: you need dishes with high ferromagnetic properties, that is, metal dishes with the ability to magnetize. As a rule, cookware for induction is specially marked with the word “Induction” in the translation “induction”, or with a zigzag symbol. But if the manufacturer is a no-name, and there is no marking, you just need to put a magnet to the bottom of the dishes: if it sticks, everything is in order, the dishes will work.
There is also an adapter for induction cookers - it allows you to cook in aluminum, ceramic and glassware.
The technical passport of the device indicates that the size of the dishes should not be half the burner, otherwise electromagnetic waves can affect everything that is nearby - electrical appliances or people.

The thickness of the bottom of the cookware for the induction cooker must be at least 2 mm
Device principle induction hob fundamentally different from the device of a classic electric stove.
The cooker works on the principle of a transformer - an induction coil is located under the glass-ceramic panel as the primary winding, and the flow of inductive energy passes through it. Its frequency is approximately 20-60 kHz. As a secondary transformer winding is the utensil, which is placed on the surface. Thus, a high-frequency electromagnetic field is created, which produces heat and transfers it to the dishes and its contents. Items near the hob, as well as the burner itself, do not heat up.
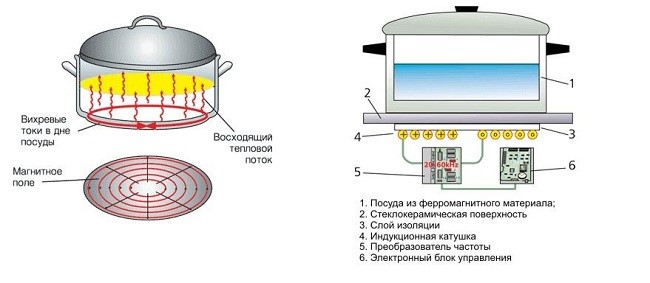
Induction Cooker Algorithm
Induction panels can vary in the following ways:
- in its performance;
- by the number of circuits;
- by the presence or absence of the oven;
- the size of the hob;
- by the presence of a control system for controlling the heating temperature.
Induction hob power consumption: how is it determined?
Most induction cookers have 4 burners of different sizes: the smallest one consumes 1 kW, two medium-sized ones consume 1.5-2 kW, and one large one consumes 2-3 kW. The number of burners can be up to six. Each circuit is heated and regulated separately, independently of the others.
Knowing the power of burners from a technical passport, using simple calculations, you can find out how much electricity the device will consume in 10, 15 or 30 minutes.

All information can be found in the passport.
If you operate the device in accordance with all the rules, you can significantly reduce its energy consumption. Manufacturers recommend:
- use the smallest burners to brew coffee, a small portion of porridge or stewed vegetables and meat;
- the largest contour is for a large pot with borsch or a pan with fried potatoes;
- medium contours suggest cooking, stewing, etc. in medium-sized containers;
- some models have paired burners, they can use oval dishes such as ducklings;
- some devices are equipped with special express rings, which have a very high power (1.5-3 kilowatts) and are fast heating rings.
Double burner induction panel
Naturally, the more burners and the sum of their productivity, the more electricity the device will consume. If the wiring allows, it is better to purchase a stove with 4-6 electric rings with good power - this will reduce the time for cooking and finding the cook in the kitchen.
If the wiring is old and its capabilities are not credible, it is better to choose a device with a consumption of up to 3.5 kW. A model with such power consumption can be connected independently by simply plugging the plug into a power outlet.
If the wiring is modern and not in doubt, you can take a model with an energy consumption of up to 10 kW, but you can’t just plug a powerful plate into a free outlet without taking into account the allowable load. In this case, individual electrical wiring is necessary to power the electric stove.
Do not use extension cords and tees to connect the induction cooker: for safe operation, it must be included in the power supply with a working ground.
Induction Type Energy Consumption Testing
Comparing the induction hob with a conventional electric stove, we can conclude that they have the same energy consumption. What is the saving?
- We will test the energy consumption of an induction hob and a classic electric stove. We take two 4-burner stoves, in which the power is 3.5 kW. On both surfaces we put two 3-liter containers with two liters of liquid at room temperature. Do not cover with lids. On a classic electric stove, water began to boil after half an hour - 3.5 × 30 = 1.05 kW per hour. At the induction after 6 minutes - 3.5 × 6 = 0.21 kW per hour.
- The next test is induction against microwave. The task is to heat a glass of milk to 50 degrees. A microwave oven heated a glass of milk in 40 seconds, a stove the same amount of milk in 30 seconds.
- The third test is the operating time of the burners.
In a quarter of an hour, the consumption of electricity by induction will be 0.175 kW per hour, only 0.5 kW per hour. In an ordinary electric stove in 15 minutes 0.175 kW per hour, but the energy consumption will be 1.93 kW per hour.
Induction Electricity Costs:
- consumption per hour - 1.3 kW;
- electrical circuits - 4 pieces;
- operation two hours a day for a month - 0.5 × 1.3 × 4 × 2 × 30 = 156 kW;
- operation 2 hours a day for a year - 0.5 × 1.3 × 4 × 2 × 365 = 1890 kW;
- 1890 kW × 5 rubles per 1 kW = 9450 rubles during the year.
The cost of electricity of a classic electric stove:
- consumption per hour - 1.3 kW;
- electrical circuits - 4 pieces;
- operation two hours a day for a month - 1.93 × 1.3 × 4 × 2 × 30 = 602 kW;
- operation 2 hours a day for a year - 1.93 × 1.3 × 4 × 2 × 365 = 7362 kW;
- 7362 kWh × 5 rubles per 1 kW = 36810 rubles during the year.
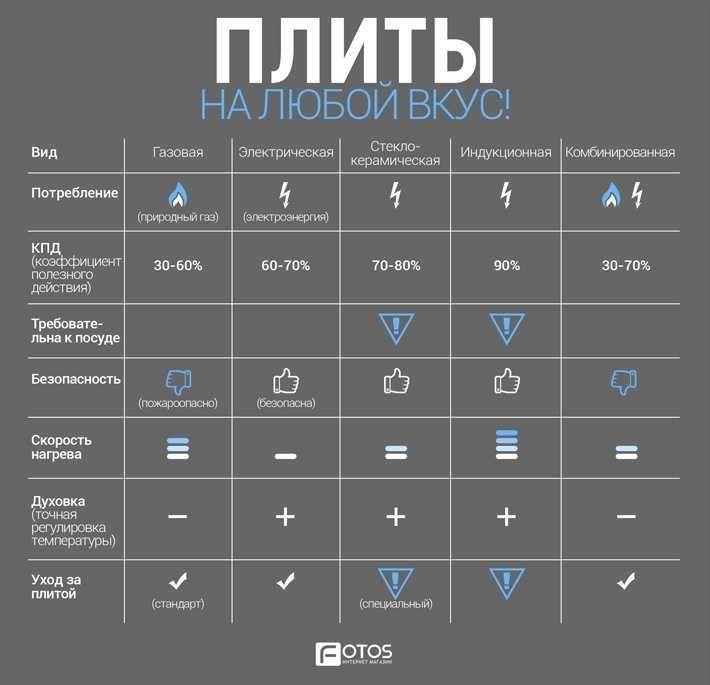
Induction cooker efficiency is the highest
It turns out that in comparison with the energy efficiency of a classic electric stove, induction is 5 times more efficient.
So the answer is found. The savings with this device are in its high efficiency - 90% (due to the absence of leakage of temperature heating outside the dishes). By the way, the efficiency of a classic electric stove is 60%, gas - 40%. That is, the whole point is over how long the Nth amount of electricity is used. The smaller it is, the less electricity will be consumed. Energy saving occurs by reducing the time of its use. Also, when removing dishes from the surface, it instantly turns off, which also saves electric energy.
For a certain amount of time, induction will justify the money invested in it, not to mention the pleasure of cooking on it.
 How to light an oven in a gas and electric stove
How to light an oven in a gas and electric stove  What is convection in the oven - the advantages of the regime
What is convection in the oven - the advantages of the regime  Can I turn off the gas stove myself and how to do it
Can I turn off the gas stove myself and how to do it  Top 10 hob 2018-2019 - the best models of famous manufacturers
Top 10 hob 2018-2019 - the best models of famous manufacturers  Compare the stove Hephaestus with Burning, Hans, Darin - which stove is better
Compare the stove Hephaestus with Burning, Hans, Darin - which stove is better 

