- How is the refrigerator
- How the refrigerator works
- The main types of cooling systems
- The principle of operation of absorption refrigerators
- The principle of operation of the self-freezing refrigerator
- Industrial refrigerators
- The principle of operation of the inverter refrigerator
- Refrigerator Thermostat Device
- A refrigerator without electricity - is it true or fiction?
Home comfort of a modern person can not be imagined without a refrigerator. It is intended for long-term storage of products. According to scientists, each family member opens the door up to 40 times a day. We look inside without even thinking how our refrigerator works.
In our article, we will consider in detail the device and the principle of operation of various refrigerators.
How is the refrigerator
Any modern refrigerator consists of the following main units:
- Engine.
- Capacitor.
- Evaporator.
- Capillary tube.
- Drain filter.
- Dokupatel.
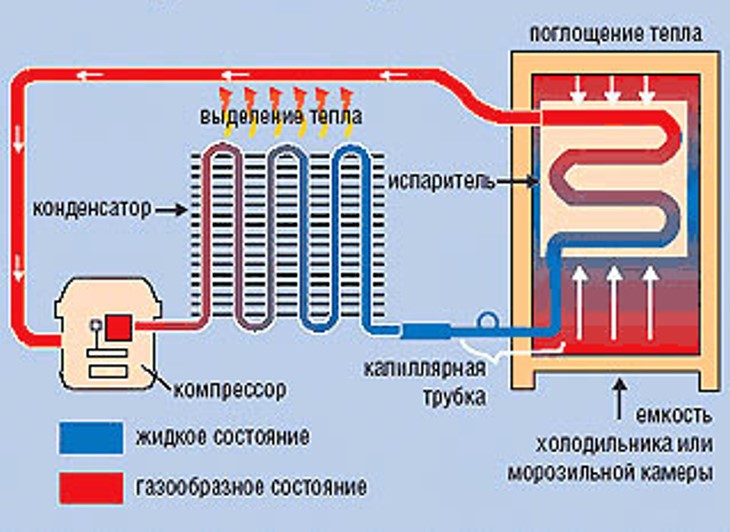
The scheme of the refrigerator
Electric motor
The engine is the main unit of the household appliance. Designed for the circulation of coolant (freon) through the tubes.
The engine consists of two units:
- electric motor;
- compressor.
An electric motor converts electrical current into mechanical energy. The unit consists of two parts - the rotor and the stator.
The stator housing is made up of several copper coils. The rotor has the appearance of a steel shaft. The rotor is connected to the piston system of the engine.
When the motor is connected to the power supply network, coils generate electromagnetic induction. It is the cause of the torque. Centrifugal force drives the rotor in a rotational motion.
Did you know that the refrigerator accounts for 10% of all electricity consumed. The open door of the appliance increases electricity consumption several times.
When the rotor of the engine rotates, the piston moves linearly. The front wall of the piston compresses and discharges the working fluid to a working state.
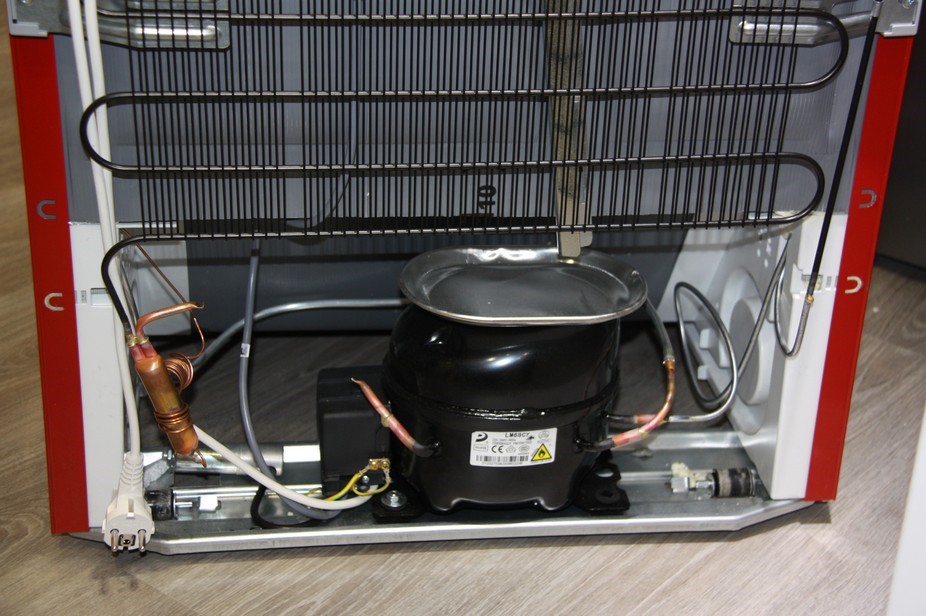

Refrigerator Engine Position
In modern cooling installations, the electric motor is located inside the compressor. This arrangement blocks the gas path for spontaneous leakage.
To reduce vibration, the engine is located on a springy metal suspension. The spring may be located outside or inside the device. In modern units, the spring is located inside the engine housing. This allows you to effectively dampen vibration during operation of the apparatus.
Capacitor
It is a serpentine pipeline with a diameter of up to 5 millimeters. Designed to remove heat from the working fluid into the environment. The capacitor is located on the rear outer surface of the device.
Evaporator
Represents a thin tube system. Designed for evaporation of the working fluid and cooling the surrounding area. Located inside or outside the freezer.
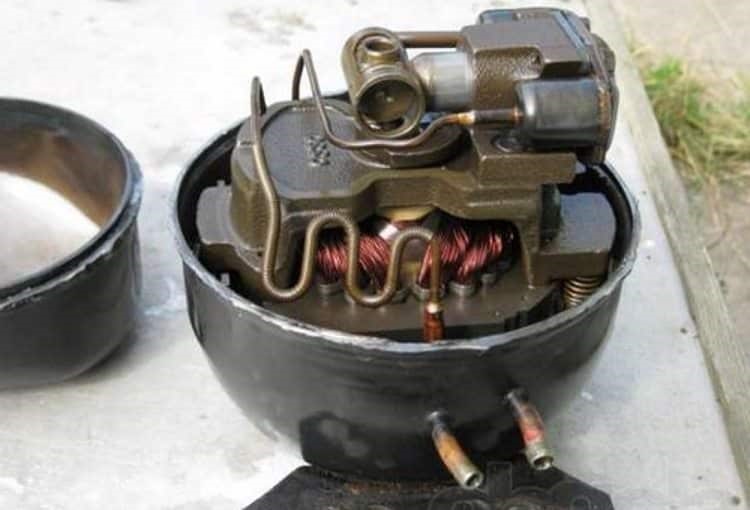

Compressor device
Capillary tube
Designed to reduce gas pressure. It has a diameter of 1.5 to 3 millimeters. Located between the evaporator and the condenser.
Filter drier
Designed to clean the working gas from moisture. It has the appearance of a copper tube with a diameter of 10 to 20 mm. The ends of the tube are elongated and hermetically soldered to the capillary tube and capacitor.
Attention! The filter drier has a one-way operation principle. The device is not intended for reverse operation. If the filter is installed incorrectly, the installation may fail.
Inside the tube is zeolite - a mineral filler with a highly porous structure.Barrier nets are installed at both ends of the tube.
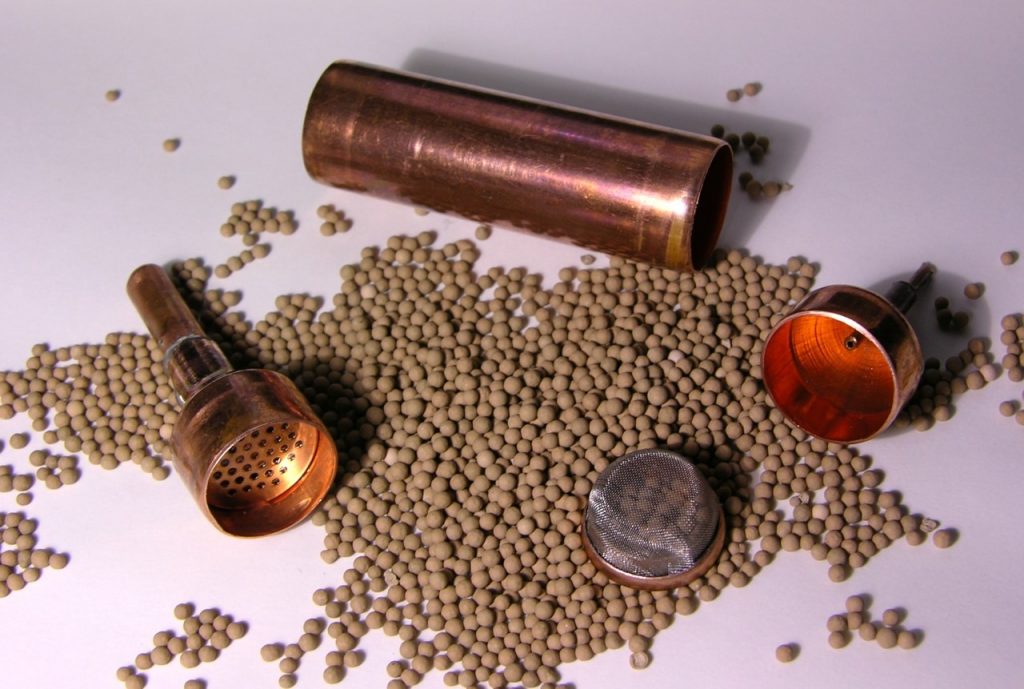

Filter drier
A metal mesh with mesh sizes up to 2 mm is installed on the side of the capacitor. A synthetic mesh is installed on the side of the capillary tube. Cell sizes of such a grid are tenths of a millimeter.
Dokipatel
It is a metal container. It is installed in the area between the evaporator and the compressor inlet. Designed to bring Freon to a boil, followed by evaporation.
Serves to protect the engine from liquid. The ingress of working fluid can lead to failure.
How the refrigerator works
The main principle of operation of any refrigerator is based on two work operations:
- The removal of thermal energy from the device into the surrounding space.
- The concentration of cold inside the device.
For the selection of heat, a refrigerant called freon is used. It is a gaseous substance based on ethane, fluorine and chlorine. Freon has the unique ability to switch from a gaseous state to a liquid state and vice versa. The transition from one state to another occurs when the pressure changes.
The operation of the cooling system is as follows. The compressor sucks freon inward. An electric motor works inside the device. The engine drives the piston. When the piston moves, gas is compressed.
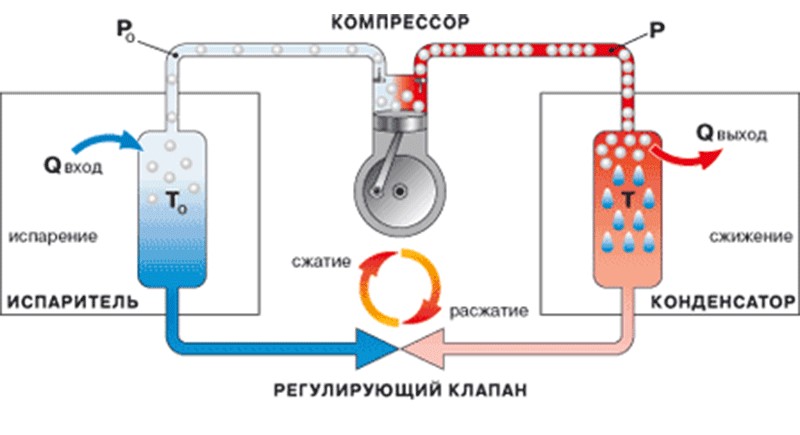
Schematic diagram of the refrigerator
The gas compression process is divided into two stages. At the first stage, the piston moves back. When the piston is displaced, the inlet valve opens. Through an open hole, freon enters the gas chamber.
At the second stage, the piston moves in the opposite direction. During reverse movement, the piston compresses the gas. Compressed freon presses on the outlet valve plate. The pressure in the chamber rises sharply. As the pressure increases, the gas heats up to a temperature of 100 ° C. The exhaust valve opens and releases gas to the outside.
Heated freon from the chamber enters an external heat exchanger (condenser). On the way along the condenser, freon gives off heat to the outside. At the end point of the condenser, the gas temperature decreases to 55 ° C.
But did you know that the very first refrigerators used sulfur dioxide as a refrigerant? Such devices were very dangerous due to the high probability of depressurization of the system.
In the process of heat transfer, gas condensation occurs. Freon from a gaseous state turns into a liquid.
From the condenser, the liquid freon enters the filter dryer. Here, moisture is absorbed by a special sorbent. From the filter, gaseous freon enters the capillary tube.
The capillary tube plays the role of a kind of plug (obstacle). At the inlet to the tube, the gas pressure decreases. The refrigerant turns into liquid. From the capillary tube, freon enters the evaporator. When pressure drops, Freon evaporates. Along with the pressure, the gas temperature also drops. At the time of entry into the evaporator, the temperature of freon is - 23 ° C.
Freon passes through a heat exchanger inside the refrigerator. Cooled gas removes heat from the inside of the evaporator tubes. When heat is released, the internal space of the refrigerator is cooled.
After the evaporator, freon is sucked into the compressor. The closed cycle is repeated.
The main types of cooling systems
According to the principle of action, the following types of refrigerators are distinguished:
- compression;
- adsorption;
- thermoelectric;
- steam ejector.
In compression units, the movement of the refrigerant is carried out by changing the pressure in the system. The pressure control of the working fluid is carried out by the compressor. Compressor cooling systems are the most common type of cooling device.
In absorption plants, the movement of the refrigerant is due to its heating from the heating system. Ammonia is used as a working mixture.The disadvantage of the system is the high danger and complexity of maintenance. This type of household appliance is obsolete and has been discontinued today.
Did you know that the very first refrigerator was launched by the American company General Electric back in 1911. The device was made of wood. Sulfur dioxide was used as a refrigerant.
The main principle of operation of thermoelectric refrigerators is based on the absorption of heat during the interaction of two conductors during the passage of electric current through them. This principle is known as the Peltier effect. The advantage of the device is high reliability and durability. The disadvantage is the high cost of semiconductor systems.
Steam ejector plants use water. The role of the propulsion system is performed by the ejector. The working fluid enters the evaporator. Here, boiling of the liquid occurs with the formation of water vapor. During heat generation, the water temperature drops sharply.
Chilled water is used to cool foods. Water vapor is discharged by the ejector to the condenser. In the condenser, the water vapor is cooled, converted to condensate and again fed to the evaporator. The advantage of such installations is their simplicity of the device, safety, environmental friendliness. The disadvantage of the steam ejection system is the significant consumption of water and electricity for its heating.
The principle of operation of absorption refrigerators
The operation of absorption devices is based on the circulation and evaporation of liquid refrigerant. Ammonia is used as a refrigerant. The role of the absorbent (absorber) is performed by an aqueous ammonia solution.
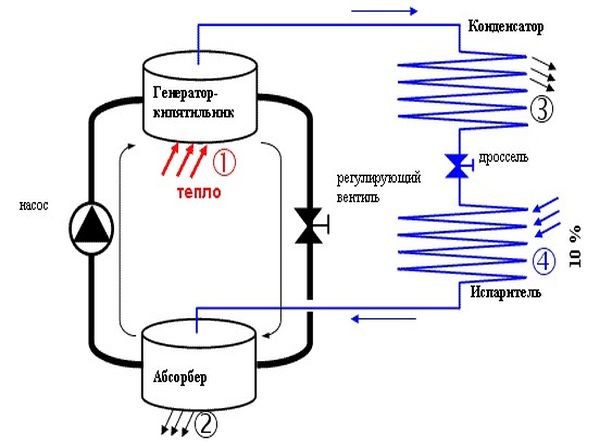
The scheme of operation of the absorption device
Hydrogen and sodium chromate are added to the cooling system of the apparatus. Hydrogen is designed to control the pressure of the system. Sodium chromate protects the inner walls of the tubes from corrosion.
Did you know that old Soviet refrigerators use chlorine-based R12 freon as a cooling mixture. The main drawback is its destructive effect on the ozone layer of the Earth.
When connected to the power supply in the generator-boiler, the working fluid is heated. The working mixture is an aqueous solution of ammonia. The ammonia solution is located in a special tank.
Heating the refrigerant leads to the evaporation of ammonia. Ammonia vapor enters the condenser. Here, ammonia condenses and turns into a liquid.
Liquefied ammonia enters the evaporator. From here, liquid ammonia mixes with hydrogen. The pressure difference of the two substances leads to the evaporation of ammonia. The evaporation process is accompanied by heat generation and cooling of ammonia to -4 ° C. Together with ammonia, the evaporator is cooled.
A chilled evaporator takes the heat of the surrounding area. After evaporation, ammonia enters the adsorber. There is clean water in the adsorber. Here ammonia is mixed with water. Ammonia solution enters the tank. The ammonia solution from the tank enters the boiler-generator and the closed cycle is repeated.
As a substitute for ammonia, aqueous solutions of acetone, lithium bromide, acetylene can be used.
The advantage of absorption devices is the noiseless operation of the units.
The principle of operation of the self-freezing refrigerator
The defrosting process in installations with a self-freezing system occurs automatically.
There are two types of self-freezing systems:
- Drip.
- Windy (No frost).
In devices with a drip system, the evaporator is located on the back of the device. During operation, frost is formed on the rear wall. When thawing, frost flows through special gutters to the bottom of the appliance. Heated to high temperature, the compressor evaporates the liquid.
In installations with a wind system, cold air from the evaporator on the rear wall is blown by a special fan inside the housing.During the thawing cycle, frost flows down the grooves into a special hole.
Industrial refrigerators
Industrial appliances differ from household appliances in the capacity of the installation and the size of the cooling chambers. The engine power of the equipment reaches several tens of kilowatts. The operating temperature of the freezers is in the range from + 5 to - 50 ° C.
Did you know that the largest industrial refrigerator occupies 24 km2 of area. This giant is located in Geneva (Switzerland) and serves for scientific purposes in the hadron collider.
Industrial plants are designed for cooling and deep freezing of a large number of products. The volume of freezers is from 5 to 5000 tons. Used at procurement and processing enterprises.
The principle of operation of the inverter refrigerator
Inverter compressors are designed for the accumulation and conversion of direct current into alternating current with a voltage of 220 V. The principle of operation is based on the possibility of smooth regulation of the motor shaft speed.
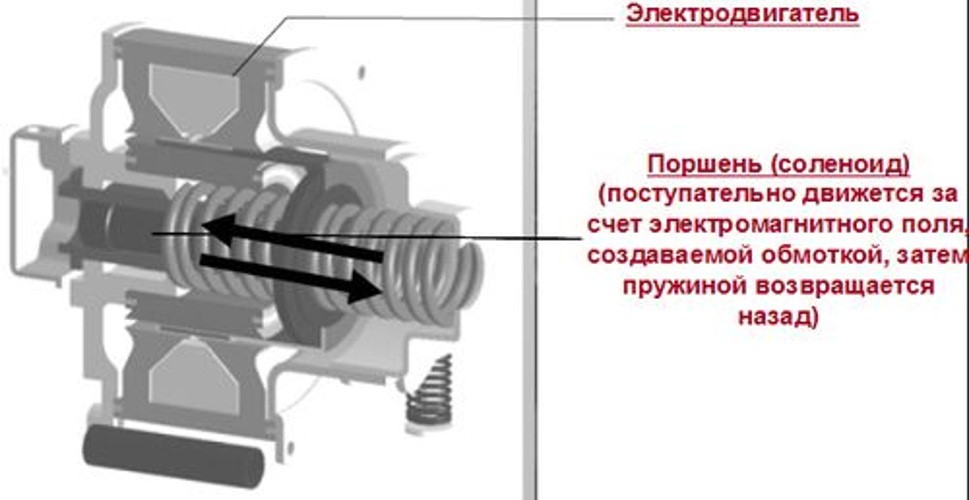
Inverter motor device
When turned on, the inverter quickly gains the required speed to create the required temperature inside the case. When the set parameters are reached, the device goes into standby mode. As soon as the temperature inside the housing rises, the temperature sensor is activated and the engine speed increases.
Refrigerator Thermostat Device
The temperature controller is designed to maintain a predetermined temperature inside the system. The device is hermetically soldered from one end of the capillary tube. At the other end, the capillary tube is connected to the evaporator.
The main element of the temperature control device of any refrigerator is a thermal relay. The design of the thermal relay consists of a bellows and a power lever.
Thermostat device
A bellows is a corrugated spring with freon in its rings. Depending on the temperature of the freon, the spring is compressed or stretched. As the refrigerant temperature drops, the spring contracts.
Did you know that modern household refrigerators use isobutane-based R600a freon. This refrigerant does not destroy the ozone layer of the planet and does not cause a greenhouse effect.
Under the influence of compression, the lever closes the contacts and connects the compressor to work. With increasing temperature, the spring stretches. The power lever opens the circuit and the motor turns off.
A refrigerator without electricity - is it true or fiction?
Mohammed Ba Abba, a resident of Nigeria, received a patent for a refrigerator without electricity in 2003. The device is a clay pots of different sizes. The vessels are folded into each other according to the principle of the Russian “nesting dolls”.
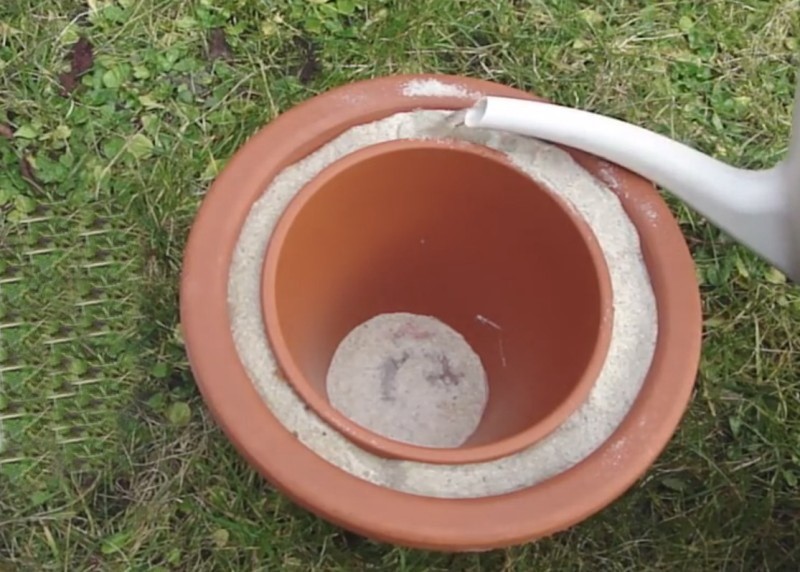

Fridge without electricity
The space between the pots is filled with wet sand. As a cover, a damp cloth is used. Under the influence of hot air, moisture from the sand evaporates. Evaporation of water leads to a decrease in temperature inside the vessels. This allows you to store food in a hot climate for a long time without the use of electricity.
Knowing the device and the principle of operation of the refrigerator will allow you to perform a simple repair of the device with your own hands. If the system is configured correctly, then the device will work for many years. For more complex malfunctions, you should contact the specialists of service centers.
 Pros and Cons of Nou Frost Refrigerators
Pros and Cons of Nou Frost Refrigerators  Refrigerator next to the stove and oven - can I?
Refrigerator next to the stove and oven - can I?  Is it possible to hang fridge magnets
Is it possible to hang fridge magnets  How to choose a good two-chamber refrigerator and features of its device
How to choose a good two-chamber refrigerator and features of its device  The water in the refrigerator does not go away and why the water does not freeze in the freezer - what to do
The water in the refrigerator does not go away and why the water does not freeze in the freezer - what to do 

