According to the standards, the voltage in household networks should be equal to 220 volts. Deviations of ± 5% are allowed. But in practice, due to the decay of networks, accidents at substations, and emergency situations, the norms are not respected. To protect home appliances from sudden surges, manufacturers recommend the use of voltage stabilizers.
However, some users believe that the need to purchase is supposedly a "marketing ploy" by manufacturers of such devices. We will figure out whether a voltage regulator is actually needed for the refrigerator, and what consequences its absence can lead to. Also in the article we will give valuable recommendations on power calculation and selection.
Why do I need a stabilizer for the refrigerator
The technical documentation for the refrigerator indicates the permissible operating voltage in the range 220 - 240V. Moreover, manufacturers guarantee the uninterrupted operation of equipment only if this condition is met. Accordingly, even if the refrigerator is under warranty, but the breakdown occurred due to an overvoltage, the manufacturer refuses its obligations regarding free warranty service. Due to the low voltage in the network, the compressor does not start, which means that the device will not work. But high voltage is fraught with burnout of expensive nodes.
In the risk zone, electronic components with special sensitivity to the quality of electric power, as well as elements of the Nou-Frost system and a motor-compressor.
Constant power surges and prolonged drawdowns in the network are the main causes of premature compressor wear. Due to long-term operation at low voltage, the motor windings overheat, breakdown of insulation, inter-turn short circuit occurs. Due to the fact that the network does not have the necessary values, the engine will not start. Moreover, the long-term effect of Ilaunch leads to overheating and subsequent combustion of the motor windings.
Quite often, the compressor seizes up after a short power outage (for a few seconds). The stabilizer will prevent all these costly breakdowns.
In order for the device in question to really protect the equipment, you need to pay special attention to the choice. Not all appliances are suitable. The device is selected taking into account the operating characteristics of the equipment (an example of calculation will be discussed below). In addition, the device must meet the following requirements:
- Designed for round-the-clock uninterrupted operation;
- large smoothing range: from 140 to 280 volts;
- wide range of operating temperatures and low noise level;
- dust and moisture proof housing.
What power stabilizer to take for the refrigerator
In the passport to the device the main technical characteristics are written, including power. But to calculate the required power, we need not the consumed, but the full power (in VA). This value is the most important characteristic when choosing a stabilizer.
To get its value, you need to divide the active power (indicated in the passport) by 0.65. But this is not enough. Since the refrigerator uses significant inrush currents, the value must be multiplied by a factor of 3.
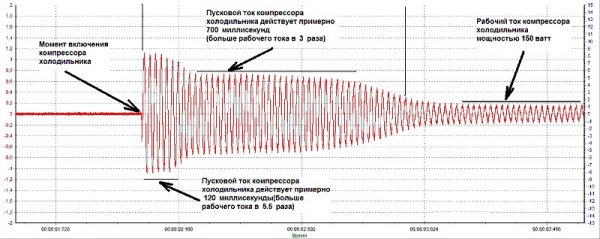
Specifications
Let's take an example. Let's say the passport states that the power consumption of the refrigerator is 0.15 kW. Then the total power is one hundred and fifty divided by zero sixty five and we get 230.76 VA.We multiply this value by 3 and we get 692.3 VA. Round the value up and get 700 VA. So, we need a stabilizer, which at the lowest output voltage will produce 0.7 kW.
Selection tips
First of all, you should decide which device for voltage equalization is needed: single-phase or three-phase. As a rule, a household network is single-phase. But there are exceptions. If there is no exact information, it is worth checking with the electrician who is servicing the network.
Devices are produced by different manufacturers, both domestic and foreign. Moreover, even in the Russian market there are several worthy firms. For example, the products of the company "Energy" or "Resanta" are very popular.
For the safe operation of the refrigerator, 3 types of stabilizers are suitable: relay, electronic-mechanical and triac. Consider in more detail the pros and cons of each type.
Relay transformers

Relay stabilizer
In relay stabilizers, as the name implies, the transformer windings are switched using power relays. In the figure we see the simplest circuit of a relay stabilizer built on the basis of comparators. The comparator is a kind of logic chip that receives 2 analog signals at its inputs: if the signal at the “+” input is greater than at the “-” input, it produces a high level signal (one relay is triggered), if the signal at the “+” input is less than at the “-” input, the comparator generates a low level signal. Thus, the transformer windings are switched.
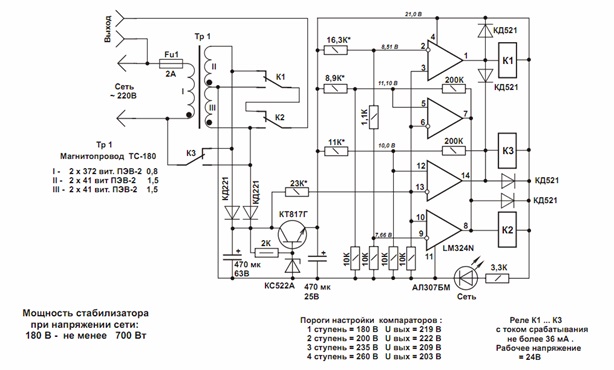
Schematic diagram of the relay stabilizer
The advantages of relay stabilizers are:
- quick response (0.5 seconds);
- low cost;
- wide limits of increased / decreased voltages.
Among the shortcomings, we note the noise of the work (due to the clicks of switching the relay), the possibility of burning contacts (if the voltage constantly jumps).
Electromechanical type stabilizers
Electronic-mechanical representatives have a control board. It monitors the voltage characteristics and controls the operation of the servo motor, which drives the current. a receiver, which, in turn, moves along the turns of the coil, thereby controlling the operation at the input.

Electromechanical voltage stabilizer
For example, consider a circuit diagram. Here, the output signals from the comparator are the inputs of RS-flip-flops, built on AND-NOT logic circuits. This allowed achieving higher accuracy (2–4%, while in relay types the error reached 8%). The disadvantages of products include low speed.
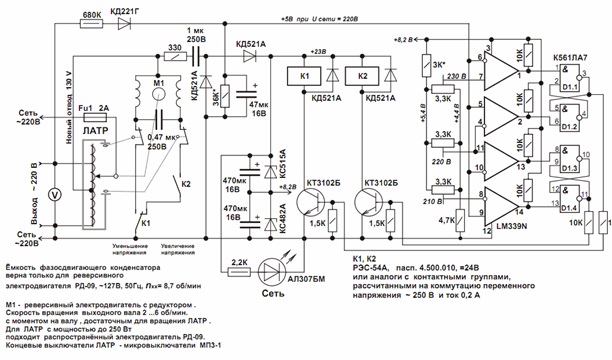
Schematic diagram of the electronic voltage regulator
Triac

Triac voltage regulator
Triac stabilizers switch windings using triacs. Oxidation of contacts and clicking sounds are excluded here, which cannot but rejoice. To date, triac stabilizers are the most reliable and durable, they have low errors (no more than 3%).
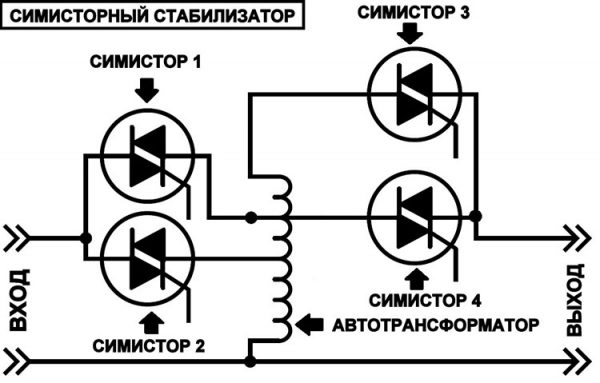
Simplified circuit diagram of a triac stabilizer
If the voltage surges often - this is the best option for protecting the refrigerator. The only drawback of devices of this type: high price, compared with relay and electromechanical types of stabilizers.
 Pros and Cons of Nou Frost Refrigerators
Pros and Cons of Nou Frost Refrigerators  Refrigerator next to the stove and oven - can I?
Refrigerator next to the stove and oven - can I?  Is it possible to hang fridge magnets
Is it possible to hang fridge magnets  How to choose a good two-chamber refrigerator and features of its device
How to choose a good two-chamber refrigerator and features of its device  The water in the refrigerator does not go away and why the water does not freeze in the freezer - what to do
The water in the refrigerator does not go away and why the water does not freeze in the freezer - what to do 

