It is convenient to get boiling water or just hot water in different conditions use electric boilers. They differ in the volumes of the heated fluid, in functional types and in productivity. An essential characteristic of each heater is the value of the energy it consumes, that is, power. But it is also important to know what current the boiler consumes. The possibility and use of the device in specific operating conditions depends on the type and magnitude of the current.
Produced boilers can be divided into three types.
Immersion Boilers
The simplest, cheapest and long-known type of device for boiling. Designed to produce boiling water in the smallest volumes. In fact, they are used to boil no more than 1 liter of water, that is, 1 - 2 cups.
The main model is a metal heating coil with a cable to connect to an electricity source. The spiral is lowered into a container of water and removed at the end of boiling.
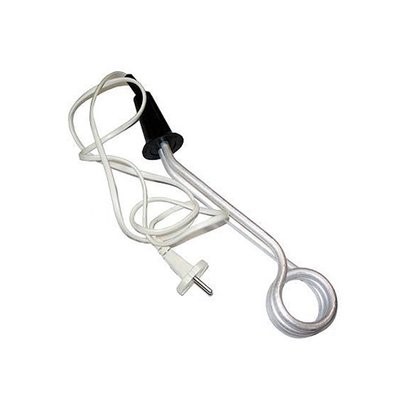

Conventional immersion boiler
The capacities of commercially available boilers are from 500 to 1500 watts, rarely more. The use of submersible electric boilers of greater power is hardly justified. The current consumption from the network 220 volts does not exceed 10 amperes. The performance of such devices is low. It may take 5 to 10 minutes for a 500-watt appliance to boil .5 - 1 liter. But for a single boil of 2 liters, an electric boiler with a power of 1.5 kilowatts is already needed.
Models are also produced in the automotive version - with DC power 12 V or 24 V, and equipped with a plug for the cigarette lighter socket.

Submersible boiler with car plug
It is, of course, convenient for driving to nature, but its performance is even less. These models typically consume 120 watts, and it may take more than 10 minutes to get 0.5 liters of boiling water.
Variants of combining a low-power heating element with a small volume (0.5 - 1 l) for water are often called a "boiler-circle". But it would be more correct to consider this device as a mini-kettle.
Benefits
- Small sizes. It can be taken with you on trips and used where other heating devices are not available.
- Low cost
disadvantages
- Low power and performance
- In addition to the heater itself, you also need dishes in which it immerses
- Lack of protective features on most models
- Fire hazard
Bulk Boilers
The main feature of this type of powerful devices is that they do not connect to the water supply network. Water must be poured into them manually or using primitive pumps. They are produced with volumes of heated water from 5 to 40 liters, which allows them to be used both in industrial and in domestic conditions. But the most effective is their use in small food outlets - cafes, bars. Also convenient for general use by employees of small firms. They are powered from an electric network with a voltage of 220 volts.
The power of heating elements in different models is from 1 to 3 kW, which corresponds to a current consumption of 5 - 15 amperes.
To achieve a capacity of 30 l / h, a heating element with a power of 2.5 to 3 kW is required.

3.2 kW bulk boiler with a capacity of 30 l / h
The productivity of boilers with a power of 1 - 1.5 kW is almost not indicated in their characteristics. But, usually it does not exceed 15 - 20 liters per hour.

1.15 kW bulk boiler
Most of these units operate on the principle of "Thermal sweat", That is, after heating the water to the desired temperature, they maintain the temperature of the entire volume in a given range. They are equipped with temperature controllers for setting different temperature levels. Protective devices prevent the unit from operating when water is low.
One of the varieties is an electric geyser type boiler for making tea or coffee. Outwardly, they are almost no different. In geyser models, the strainer installed in the upper part is surrounded by hot steam from boiling water. This method is used for varieties of coffee and coarse tea.
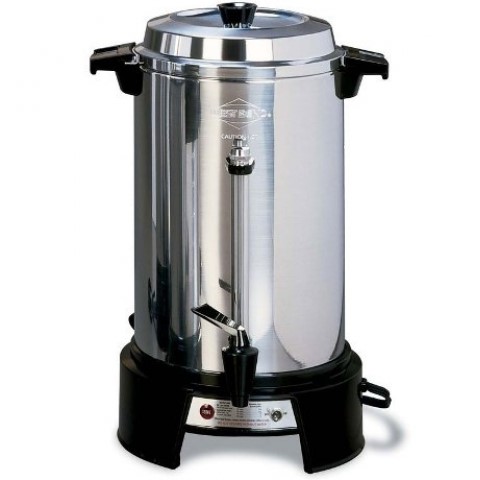

Geyser type boiler
Benefits
- Mobility. The fact that the device is not tied to the water supply allows it to be used outdoors. It is enough to have a network of 220 volts.
- Thrift. Relatively low power consumption and the absence of the need for continuous operation of the heating elements.
- Low cost among industrial types
disadvantages
- Manual topping up. It is necessary to monitor the water level in the device and take water from somewhere and add to the tank.
- Low productivity. But for institutions with the number of visitors of 20 - 30 people, they are quite effective.
Flowing Boilers
The main difference is the constant connection of the electric boiler to the water supply, therefore they are also called constant-acting boilers. This type includes the most powerful and productive industrial options. They are able to ensure the constant availability of hot water in large volumes - up to 100 liters per hour or more. The main application is large catering and other public organizations serving hundreds of people.
In such systems, automation monitors the presence of water in the heater. When using ready boiling water, the volume is automatically replenished and the heating process is resumed. Drain condensation must be provided.
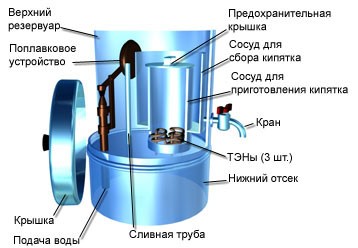
An approximate arrangement of a flowing boiler
Modern models work on the principle of step heating. Part of the volume in a separate tank is heated to maximum temperature, from which it is taken for use. This mode leads to energy savings and does not allow multiple boiling. The use of a mixer in the outlet valve allows diluting boiling water with cold water.
Available both in the desktop version and in the stationary wall version.
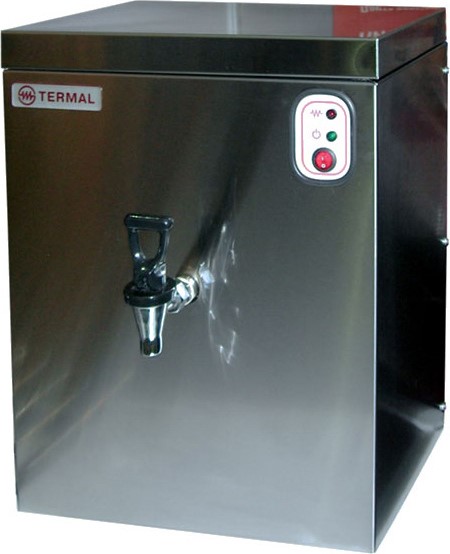

5 L flow-through wall-mounted boiler with a capacity of 12 kW 380 V and a capacity of 110 l / h
There are models with 220 volts connected to the mains, but the most powerful ones require a 3-phase network with a voltage of 380 volts. Heating elements consume from 5 to 20 kW. Such powers require a current of tens of amperes. Household wiring can not always pass such currents.
But there are instantaneous mini-heaters with a capacity of 3 - 10 liters. Obviously, cheaper liquid boilers can also heat 5 liters of water. The choice of a flow type with such volumes is determined by the convenience of their use. Despite the small volume and power of 2–3 kW, it can provide boiling water up to 20 liters per hour in the absence of any worries with topping up. The advantage of such small devices is the connection to a 220 V power supply.

A flowing boiler with a volume of 3 liters and a capacity of 2 kW 220 V
But to achieve a productivity of many tens of liters per hour, the power of the heaters must be at least 10 kW. For example, a 13 kW instantaneous boiler produces up to 120 liters of boiling water per hour.
And one of the most productive - 180 l / h - consumes 19.2 kW of energy.
Such devices are connected only to a three-phase network of 380 V.

Flowing boiler with a capacity of 180 l / h and a capacity of 19.2 kW 380 V
Benefits
- Large volumes and high productivity
- No manual topping
- Full automation of the entire heating and boiling process.Maintaining the water level, set temperature, draining excess portions, shutting down in emergency situations - everything is provided by the corresponding automation systems.
disadvantages
- The need to connect to industrial networks
- High power consumption
- High cost
 Thermopot does not pump water - do-it-yourself thermopot pump repair
Thermopot does not pump water - do-it-yourself thermopot pump repair  How to fix a thermal sweat with your own hands: causes and their elimination
How to fix a thermal sweat with your own hands: causes and their elimination  Best electric kettles - TOP-10 for 2019
Best electric kettles - TOP-10 for 2019  Which electric kettle is better to choose? Rating of the best electric kettles
Which electric kettle is better to choose? Rating of the best electric kettles  The water supply button on the thermal sweat does not work - what should I do?
The water supply button on the thermal sweat does not work - what should I do? 

