A microwave oven has become firmly established and has become one of the indispensable attributes of any apartment. This household appliance allows you to heat or cook food in a matter of minutes with the help of radiation invisible to the eye.
But in order to find out where this radiation comes from and how safe it is for humans, it is necessary to understand the device and the principle of operation of a microwave magnetron, which is a generator of high-frequency waves.
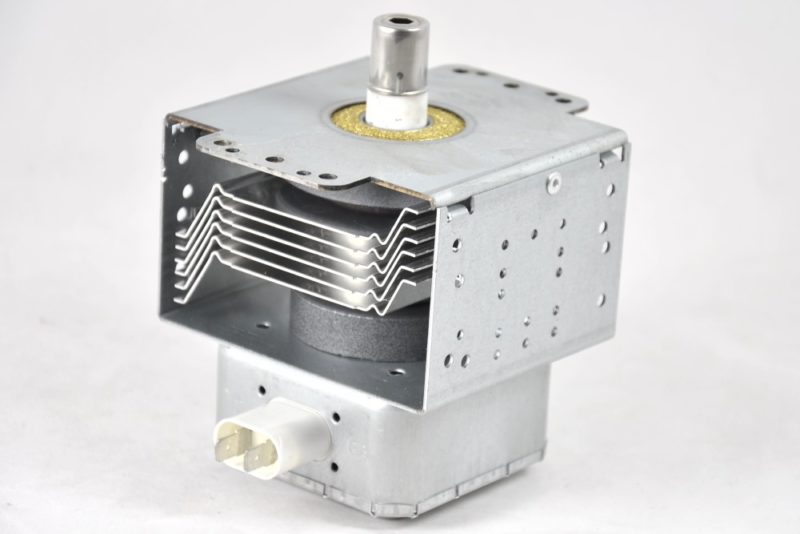

Magnetron
What are microwaves and how do they heat food
Microwave radiation is called electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 1 mm to 1 m. This type of radiation is used not only for domestic purposes, but also in navigation and radar systems, and in addition, it provides cellular communications and satellite television.
Microwaves can be generated both artificially and naturally (for example, on the Sun). Another name for microwaves is microwave radiation, or microwave.
All types of household microwave ovens have a single radiation frequency of 2450 MHz. This value is an international standard that home appliance manufacturers must strictly adhere to so that their products do not interfere with the operation of other microwave devices.
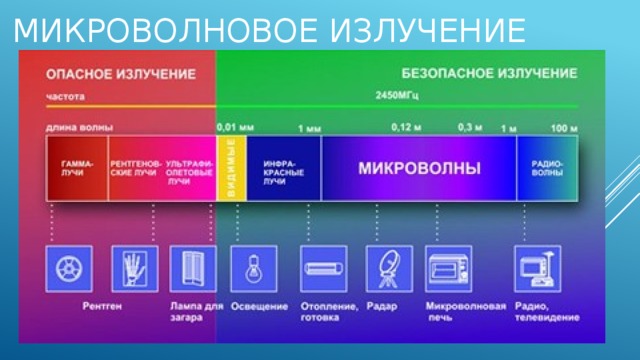
Microwave radiation
The thermal effect of microwave radiation was discovered by the American physicist Percy Spencer in 1942. It was he who patented the use of a device that generates microwaves for cooking, thereby laying the foundation for the use of microwave ovens in everyday life.
Over the next few decades, this technology was perfected, which allowed to establish a mass production of simple and inexpensive devices for fast food warming.
In order to heat any material in a microwave oven, the presence of dipole molecules, that is, molecules having opposite electric charges at both ends, is necessary.
In foods, their main source is water. Under the influence of microwave radiation, these molecules begin to line up along the lines of force of the electromagnetic field, changing their direction about 5 billion times per second. The friction between them is accompanied by the release of heat, which heats the food.
However, microwaves are not able to penetrate deeper than 2-3 cm from the surface of the product, therefore everything that is under this layer warms up due to thermal conductivity from the heated areas.
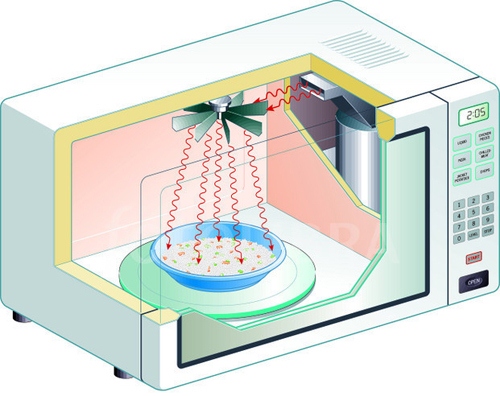
Microwave heating
Magnetron device and its application
In most types of microwave technology, a magnetron is a generator of microwave frequencies. Devices that are similar in their principle of action - klystrons and platinumotrons, are not so widely used. The magnetron was first used in microwave ovens in 1960. The most commonly used technique is a multi-cavity magnetron, consisting of several components:
- Anode. It is a copper cylinder, divided into sectors with thick metal walls. These volumetric cavities are the resonators creating the ring oscillation system. A voltage of about 4000 volts is applied to the anode.
- Cathode. It is located in the central part of the magnetron and is a cylinder, inside of which there is an incandescent filament.Electron emission occurs in this part of the device. A voltage of 3 volts is applied to the heater (filament).
- Ring magnets. Electromagnets or permanent magnets of high power located in the end parts of the device are necessary to create a magnetic field directed parallel to the axis of the magnetron. The movement of electrons is also carried out in this direction.
- Wire loop It is connected to the cathode, fixed in the resonator and output to the antenna emitter. The loop is used to output microwave radiation into the waveguide, after which it enters directly into the microwave chamber.
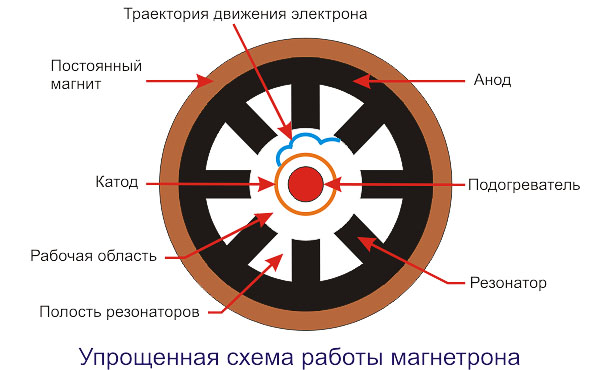
Magnetron device
Due to the simplicity of design and low cost, magnetrons have found application in many areas, but they are most common:
- In microwave ovens. In addition to quick cooking and thawing food in domestic ovens, magnetrons also allow you to perform production tasks. An industrial microwave oven can carry out heating, drying, melting, roasting and much more. It is important to remember that the microwave cannot be turned on empty, because in this case the radiation will not be absorbed by anything and will return back to the waveguide, which can lead to its breakdown.
- In radar. The radar antenna connected to the waveguide is actually a conical feed and is used in conjunction with a parabolic reflector (plate). The magnetron generates powerful short energy pulses with a small wavelength, part of which, reflected, again goes to the antenna and then to the sensitive receiver, which processes the signal and displays it on the screen.
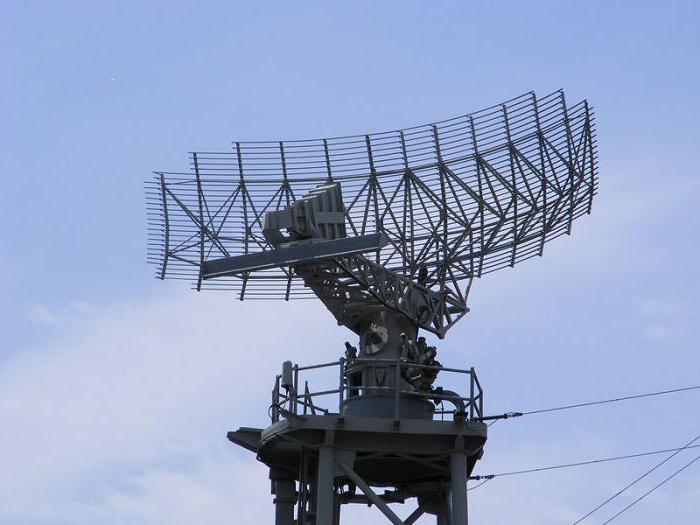

Magnetrons in radar
The principle of operation of the magnetron
The operation of the microwave oven is based on the conversion of electrical energy into electromagnetic radiation of ultra-high frequency, which drives the water molecules in food. Dipole molecules, constantly changing direction, produce heat, which allows you to quickly heat products, while maintaining their beneficial properties. A device that generates microwaves is a magnetron.
The magnetron, in fact, is an electro-vacuum diode, in the operation of which the phenomenon of thermionic emission is applied. This phenomenon occurs during the heating of the surface of the emitter or cathode. Under the action of high temperature, the most active electrons tend to leave its surface, but this will only happen when voltage is applied to the anode. In this case, an electric field arises, and the electrons begin to move towards the anode, moving along its lines of force. If the electrons are in the magnetic field, then their trajectories deviate in the direction of the lines of force.
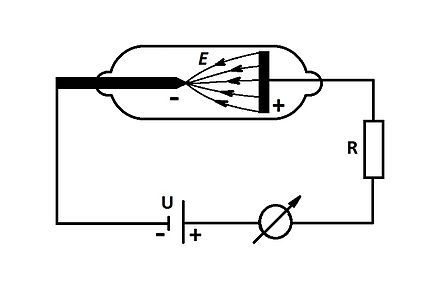
Vacuum diode
The magnetron anode has the form of a cylinder with a system of cavities, or resonators, inside of which there is a cathode with a filament. Two ring magnets located along the edges of the anode create a magnetic field inside the anode, due to which the electrons do not move directly from the cathode to the anode, but change their path, rotating around the cathode. Near the resonators, the electrons give them part of their energy, which leads to the formation of a powerful microwave field in their cavities, which is brought out through a wire loop connected to the emitter antenna.
To actuate the magnetron, it is necessary to apply a high voltage of the order of 3-4 thousand volts to the anode. Therefore, the magnetron is connected to a household electrical network through a high-voltage transformer. In addition, the microwave oven switching circuit includes a waveguide that transmits radiation into the chamber, a switching circuit, a control unit, as well as protection and cooling elements. In addition, the inner walls of the chamber and a thin metal mesh on the door of the device prevent the exit of radiation beyond it.
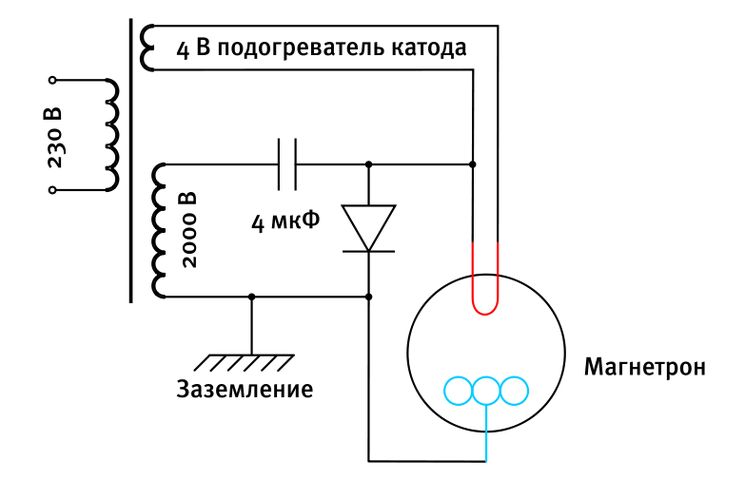
Magnetron switching circuit
How a magnetron affects microwave power
Most modern manufacturers of microwave ovens offer the option of choosing the power of the device. In turn, the operating mode (defrosting or heating) and the heating rate of food depend on this parameter. However, the design features of the magnetron do not allow reducing its power, therefore, to reduce the intensity of heating, power is supplied to it at certain intervals. These pauses in the operation of the magnetron can be seen if you turn on the microwave at medium power and listen to the sound of its work.
Not so long ago, some manufacturers of household appliances announced the appearance of a number of models of microwave ovens with an inverter power supply circuit. The application of this scheme allowed not only to increase the amount of usable space in the chamber by reducing the dimensions of the emitter, but also to reduce the power consumption of the device. Unlike conventional models, the heating temperature in inverter-type furnaces changes smoothly, but their cost is much higher.
Magnetron cooling and protection
During operation, the magnetron emits a large amount of heat, so a radiator is installed on its body. Since overheating is the main reason for the failure of the magnetron, other methods are also used to protect it:
- Thermal relay. This device is used to protect the magnetron, as well as the grill, if available in the model. The thermal fuse is equipped with a bimetallic plate, which can be adjusted to a specific temperature. If this value is exceeded, it bends and opens the power circuit.
- Fan. It not only blows the magnetron radiator with cool air, but also performs a number of other useful functions, such as cooling the electronic components of the device, circulating the air inside the chamber while the grill is working, and also removing hot steam out through special openings.
- Lock system. Several microswitches control the position of the microwave door, preventing the magnetron from turning on when it is open.
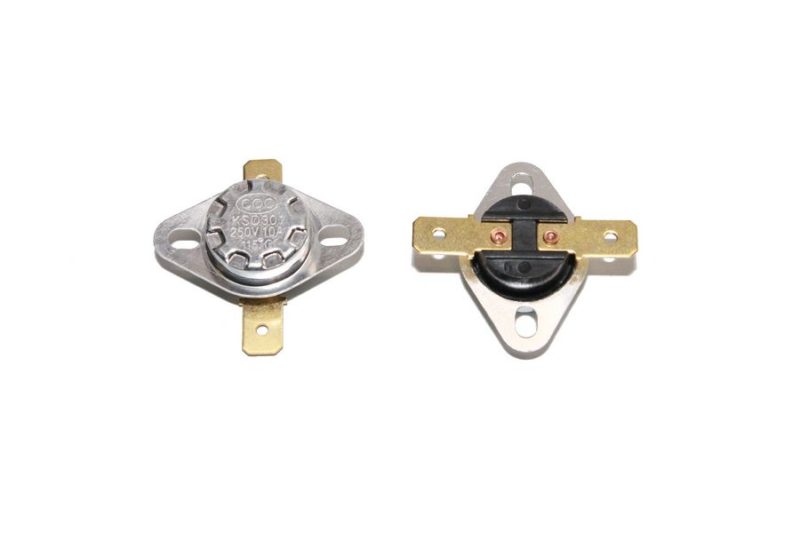

Thermal relay
Is it possible to replace the magnetron
The main advantage of modern magnetrons for household microwave ovens is their interchangeability. Magnetrons produced by other companies will be suitable for various models of microwave ovens, so they can be changed if necessary. In this case, the only necessary requirement will be power compliance. You can buy a magnetron in many electronics stores, however, in order to make the right choice, you need to understand its parameters and labeling. Most often, the following magnetron models are installed in microwaves:
- 2M 213 (600 watts of rated power and 700 watts under load);
- 2M 214 (1000 W);
- 2M 246 (1150 W - the highest power).
Even having studied all the necessary parameters of this device, it is not recommended to replace the magnetron at home. Firstly, it will be quite difficult to remove it yourself, and secondly, only a qualified specialist can ensure its safe operation after installation.

Standard magnetron configuration
Diagnostics of malfunctions and the reasons for their occurrence
Replacing a magnetron can require quite substantial financial costs, so before buying a new device, you must diagnose the old one to make sure that it is really malfunctioning. Verification can be performed at home using a conventional tester. This will require:
- Unplug the microwave.
- Remove the protective cover and visually inspect the part.
- “Ring” the main elements of the printed circuit board using a tester or “multimeter”.
- Inspect the thermal relay.
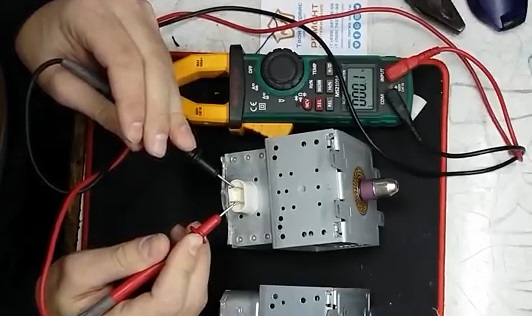
Diagnostics
At the end of the diagnosis, you can draw conclusions about the malfunction of certain parts. The main reasons for the failure of the magnetron include the following:
- Faulty vacuum cap.You can replace it yourself by simply picking up a similar cap from another magnetron. The seats of these caps have a standard configuration.
- Heater breakage. At turning on the empty microwave or improper loading of the magnetron will overheat, which can lead to excessive filament and breakage. For its diagnosis, it is necessary to measure the resistance between the legs of the capacitor. If its value is in the range of 5-7 Ohms, then the heater is working.
- Breakdown of the passage capacitor. If the tester does not show an “infinite” resistance value between its contacts, then the capacitor must be replaced.
 Why the microwave does not work and how to fix it
Why the microwave does not work and how to fix it  Magnetron sparks in the microwave - how to check and replace
Magnetron sparks in the microwave - how to check and replace  Odor from the microwave: how to clean with proven products
Odor from the microwave: how to clean with proven products  All about microwave grilling: what is it and how to use the function
All about microwave grilling: what is it and how to use the function  How many kilowatts a microwave consumes
How many kilowatts a microwave consumes 

