Often during repair work or during experiments, it is necessary to measure the temperature of the medium by immersing a measuring device in it. Such measurements require a liquid thermometer.
Thermometers the technical ones, which are based on the liquid system (heating the working fluid), are often made of ordinary glass, and therefore are extremely fragile.
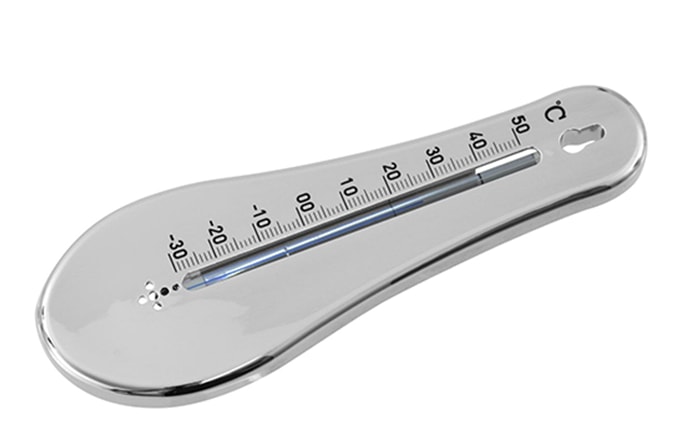

Household Liquid Thermometer
Liquid thermometer (for example, the popular TTZh M or TS-7-M1) is used in everyday life, on the streets, inside buildings, in hospitals.

Thermometer with a curved channel for taking readings in boilers and pipes
What is a liquid thermometer. Principle of operation
Thermometric measurement is based on the principle of thermal expansion of liquids.
Technical thermometer consists of 5 components:
- ball;
- liquid;
- capillary;
- overflow chamber;
- scale.
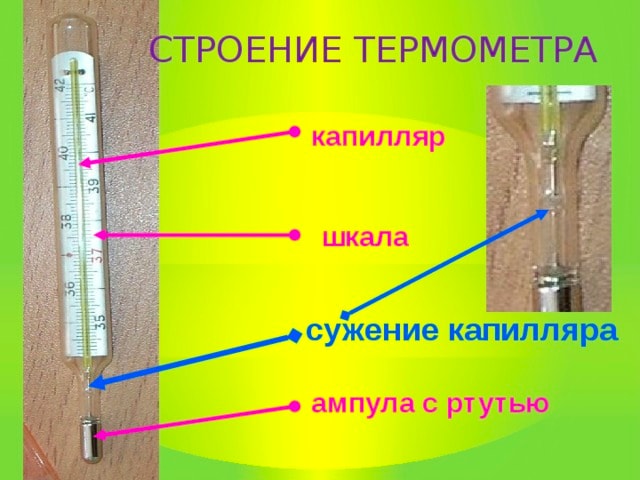
Thermometer structure
The ball is that part of the device where the liquid is placed (for example, mercury, kerosene or alcohol). A capillary is a narrow cylindrical channel. Due to the strong temperature increase (for example, in hot countries, where the temperature reaches 43-45 degrees), simple mercury thermometers may burst. The liquid expands so much that the volume it occupies exceeds the volume of the ball and capillary. Therefore, many thermometers provide a bypass chamber - a special space into which excess liquid flows.
Liquid-type thermometers are classified according to the types of liquids used: mercury, alcohol, kerosene, mercury alloys, methylcarbitol, etc.
Mercury is distinguished by a metal column, red columns of household thermometers are most often components of alcohol structures (red or blue dye is added to alcohol to make it easier to take readings). Adding dyes changes the temperature characteristics of the mixture.
Using mercury allows you to operate the device in a wide range: from -39 to +600 degrees Celsius. Mercury has a high freezing point, so using it below -35 degrees is already inefficient, since the metal goes into a completely solid state and stops responding to lower temperatures.
The evaporation temperature of mercury is quite low, and therefore it can be used even at high temperatures. Above 600 degrees, mercury turns into a pure metal gas and stops expanding, as it tends to go into a plasma state.

Mercury is a liquid metal that is part of many thermometers
Using some mercury alloys, it is possible to expand the lower measurement threshold, thereby drastically lowering the upper threshold. Thermometers based on the compression and expansion of such alloys allow measurements at temperatures from -60 to +120 degrees Celsius.
Alcohol liquid thermometers allow measurements from -80 to a boiling point of water +100 degrees.
There are thermometers that are designed to take the temperature readings of liquids, such devices are designed for immersion. These can be devices with full immersion or partial. The latter below, where the capillary is located, has a mark to which the device should be immersed so that the readings are as accurate as possible.
Read also: what are mercury free thermometers and how do they work.
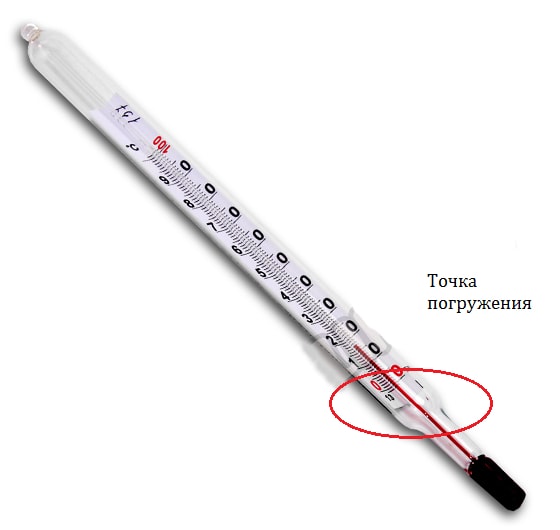

Dive point
This mark allows you to compensate for jumps in air temperature, which directly affect the liquid.
Liquid thermometers are widely used in enterprises and factories to take temperature readings of liquid solutions and substances flowing through process pipes. Such procedures complicate the measurement of fluid temperature due to insufficient access. In tubes and reservoirs create special measuring channels for inputting the device and taking readings.
Terms of Use and Precautions
Thermometers consist mainly of glass and liquid. They are dangerous for two reasons: broken glass and toxicity of the active substance.
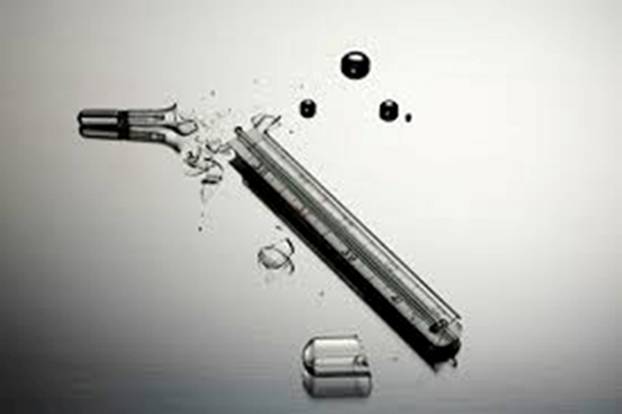

Mercury is a very toxic substance.
In the chemical industry, mercury or alcohol thermometers are more often used. Laboratory experiments require high accuracy, and liquid devices allow you to perform procedures at the highest level. A large volume of mercury is used for this. When working with such devices, a special tray should be kept under the thermometer to collect mercury as soon as possible.

The key to a broken thermometer is to quickly collect mercury
Falling from a height of human growth, mercury quickly splits into many balls and scatters in all directions. Balls of toxic liquid metal fall into the floor slots, into all holes and cracks.
Mercury is a very flowing metal. To assemble it completely is not an easy task. Gradually, mercury begins to evaporate, creating a dangerous toxic background. Ventilating a room from mercury vapor is not easy, since mercury vapor is a very heavy gas.
The procedure for removing mercury from a room is called demercurization.
If the thermometer crashes, all work must be stopped immediately; mercury must be removed immediately. Mercury removal means the following:
- All visible mercury should be removed immediately. There are two cleaning methods - a rubber bulb and a cotton swab. When swabbing, remember that the swab should be oiled.
- All mercury collected must be transferred to a special service. Mercury can not be poured into the sewer, it is much heavier than water.
- The place where the mercury was spilled should be treated with a 20% solution of iron (III) chloride, and then wait for complete drying.
- After a day, the surface should be wiped with a detergent and clean water.
Pros and Cons of Liquid Thermometers
The main disadvantages of the devices are the insecurity of liquids in the event of depressurization (especially in the case of toxic mercury) and the inability to use in extremely low or high temperatures.
The division price of most thermometers is 1-2 degrees Celsius. This allows you to make calculations quite accurately, but the temperature range of each model has its own.
The advantages of liquid thermometers is a wide scope - both for domestic and medical purposes, as well as air, steam, gas and power plants.
Popular models of liquid thermometers, their prices and comparison
The most popular are TTZh-M isp4, SP-1, BT-52.220 and TS-7-M1 isp1 devices.
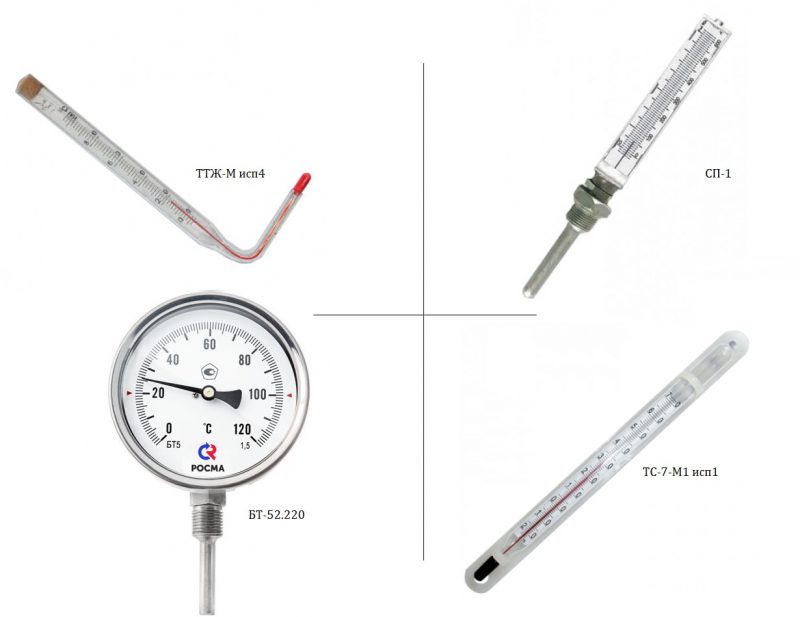

Popular liquid devices: TTZH-M isp4, SP-1, BT-52.220 and TS-7-M1 isp1
TTZH-M isp4
The thermometer is manufactured by the company Steklopribor. The L-shaped form provides for taking readings in various boiling devices with a provided valve. The average price of a device is 350 rubles.
The active substance is kerosene, the scale mark is 2 degrees. The length of the immersion is 6.5 cm, the measured range is from 0 to +100 degrees Celsius.
TS-7-M1 isp1
The device belongs to the budget class - the price varies from 250 to 300 rubles. It is used mainly in agriculture. The working fluid is methylcarbitol, the measured temperature limit is from -20 to +70 degrees Celsius. The length of the immersion is only a few centimeters.
BT-52.220
Bimetallic device, Designed specifically for aggressive environments that are found in oil, food and chemical industries.
It is steady against corrosion, allows to change temperature ranges. The average price is 1200 rubles.
Thanks to interchangeable sleeves, the length of the immersion can vary from 6.4 to 25 cm. The minimum range is from -45 to 0 degrees Celsius. The maximum is from 0 to +450 degrees.
The device was developed by Rosma. The sleeves of this device are made of brass and stainless steel. The device operates at an ambient temperature in the range from -10 to +60 degrees. The dial is made of aluminum. The device is equipped with a radial scale and an arrow.
SP-1
Liquid device manufactured by Thermopribor. The average price is about 2000 rubles.
The device only works in the positive ranges. The design allows you to use four ranges: the minimum - from 0 to +100 degrees Celsius, the maximum - from 0 to +300 degrees.
The device is resistant to vibrations, used in workshops, in machine-building factories. The working fluid is mercury.
 Overview: how to dispose of a mercury thermometer?
Overview: how to dispose of a mercury thermometer?  How to use an electronic thermometer - instructions for use
How to use an electronic thermometer - instructions for use  Rectal thermometer - what is it and what are the rules of use
Rectal thermometer - what is it and what are the rules of use  All kinds of thermometers for measuring body temperature
All kinds of thermometers for measuring body temperature  Step-by-step instruction: how to calibrate an infrared thermometer
Step-by-step instruction: how to calibrate an infrared thermometer 

