Immediately determine:
- The power of an air conditioner is the cooling capacity of an air conditioner, or the cooling capacity and heat output of a split system. Measured in BTU / h (British thermal unit) or kilowatt / hour.
- Rated power - the amount of electricity consumed by an air conditioner or split system in 1 hour.
- Recommendations are given for domestic and office premises for non-industrial purposes.
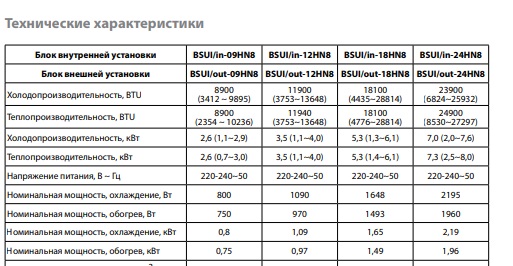
Specifications are given in two measurement systems (in the English measurement system and in metric)
To find out the power consumption of the device, you need to calculate its cooling capacity.
We will calculate the total power of the air conditioner for the server ourselves. Need to know:
- The volume of the room.
- Light level.
- The average number of people in a room or office.
- The number and power consumption of electrical equipment operating in the room.
To calculate the volume of the room, we multiply the area by height.
There is the concept of heat gain, depending on the level of illumination. For rooms it is equal to:
- For shaded 30W / m2.
- For an average lighting level of 35W / m2.
- For well-lit 40W / m2.
With an increase in the glazing area in a ratio of 2: 1 (two square meters of glazed surface to 1m2 area), the heat gain for the sunny side can reach 150 - 200 W / m2.
The total value of the heat gain of the room is found by the formula: the product of the volume by the light factor is divided by 1000 (Qpom = V * g / 1000). The resulting value is measured in kW / h.

From these values the total heat gain of the room
Intensive air circulation gives an increase in heat gain by another 20-25%. This value is calculated under the condition that the difference between the temperature inside the building and the external air temperature of 11 ° C and humidity 50%, a single complete change of air occurs. If the building is equipped with forced ventilation and the temperature difference does not exceed 3 ° C, then this criterion can be neglected in the calculations.
The upper floor gives an increase in design values by 10-20%.
Each adult increases the heat reception of the room:
- Standstill plus 0.1 kW.
- Light load plus 0.13 kW.
- At an active load plus 0.2 kW.
The total value of the heat gain from electrical equipment is made up of 30% of the total maximum consumption of all electrical equipment.
The calculator of the cooling capacity of the air conditioner has the following form:
Q of the air conditioner = Q rooms + Q of employees + Q equipment
The deviation range of the actual refrigerating capacity from the calculated one is -5% + 15%.
Example: Let's calculate the cooling capacity of a device for a server: a room with an area of 20 m2, height 3 m., low light level, serve 2 people. The maximum declared power consumption of electrical equipment is 20kW / h.
We get 20 * 3 * 30/1000 + 2 * 0.1 + 20 * 0.3 = 8.0 kW.
The cooling capacity of the equipment should be in the range of 7.6 to 9.2 kW.
Calculation of the power of the air conditioner - how many kilowatts it consumes
Air conditioner power and rated power are two different values.
The power consumption of a split system or air conditioner is presented in the instruction manual for a separate column. Power consumption is always lower than the cooling capacity of the device. Some manufacturers indicate an EER — how many times the power consumption is lower than the cooling capacity of the air conditioner. The standard ratio ranges from 2.5 to 3.5, some samples have indicators up to 4.5.
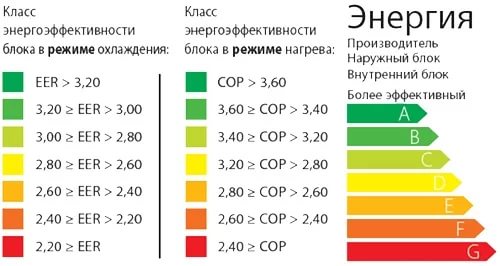
Manufacturer EER Coefficients
The power consumption of the equipment can be calculated through the EER coefficient.The cooling capacity of the device is divided by the EER coefficient, the result is the rated power.
For example: the cooling capacity of the device is 2.5 kW, the coefficient is EER 3.2, we get the rated power of 2.5 / 3.2 = 0.78 → 0.8 kilowatts.
How much (actual power consumption of the device) kilowatts per month the device consumes, we calculate this:
- We look in the operating instructions - rated power for cooling. This figure is the value of kilowatts of electricity consumed per hour.
- We calculate how many hours a day equipment works;
The number of hours can be calculated as follows: we record the operating time of the device for one hour (when it cools the air), we multiply by the time the device is turned on per day.
For example, in one hour, the device turned on twice and worked for 15 minutes. We get 15 + 15 → 0.5 hours. The operating mode of the equipment is 12 hours. 12 * 0.5 = 6 hours.
The product of the rated power for the time will give the number of kW / day. We multiply by 30 days, we get the monthly consumption. Operation of the device with open windows gives an increase in power consumption by 10-15%.
Attention! Operation of the equipment with open windows is strongly discouraged. The manufacturer guarantees the declared temperature regime only if all the requirements for operating conditions are met.
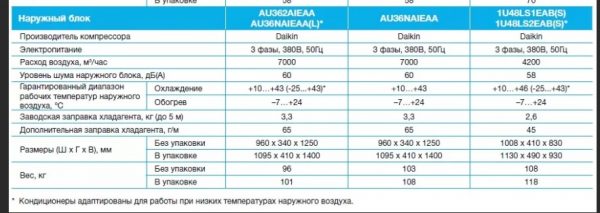
The manufacturer indicates at what outdoor temperature the device will be guaranteed to maintain the required internal temperature.
Example: A device with a nominal power consumption value of 0.8 kW, operating 4 hours a day, will consume 0.8 * 4 = 3.2 kW. For a month, expenses will amount to 3.2 * 30 = 96 kW.
The value of the capacity of the cooling system for a room of 20 square meters. meters, we calculate according to the already known formula:
- With a ceiling height of 2.75 m and one standard window on the south side of the room’s heat gain, it will be 20 * 2.75 * 40/1000 = 2.2 kW;
- Two freely moving people 2 * 0.13 = 0.26kW.
- Refrigerator, TV, computer. In order for the calculations to be economical, one computer can be considered (both devices are not used together) 0.8 + 0.75) * 0.3 = 0.465 kW.
Total total heat gain will be: 2.2 + 0.26 + 0.465 = 2.925 kW. We get the cooling capacity of the device from 2.8 to 3.4 kilowatts. With an EER coefficient of -3.0, the amount of electricity consumption will be from 0.9 to 1.1 kW / h. At 100% load 6 hours per day, the total power consumption will be up to 1.1 * 6 * 30 = 198 kW per month.
Typically, in household appliances, freon is used as the refrigerant. The manufacturer indicates the amount of refrigerant in the product passport. Its weight may not be significantly increased, it depends on the selected device when increasing the length of the trunk.

Type label and quantity of refrigerant
As mentioned above, there are two systems (metric and English). Despite the fact that BTU is not included in the international SI system, it is widely used in the labeling of air conditioners. The power in BTU (BTU) is also calculated, only the data is taken not according to the metric system, but according to the English system of measures. A British thermal unit is the amount of energy needed to heat 1 pound of water per 1˚F. The value corresponds to 0.2931 watts. Conscientious manufacturers present data in two systems at once:
- BTU cooling capacity;
- Cooling capacity kW.
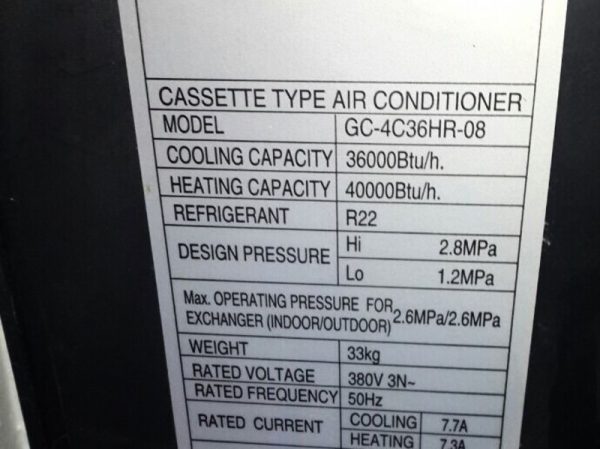
Data is presented only in BTU.
Most domestic air conditioners range from 5,000 to 18,000 BTU. For convenience, sellers classify them by the first digit of BTU refrigeration capacity. The higher the number, the greater the performance of the device. If the values are indicated only by BTU, you need to multiply this figure by 0.2931 to get the value in kilowatts.
 The device and principle of operation of the air conditioner fan
The device and principle of operation of the air conditioner fan  Air conditioning: what you need to know about its functioning
Air conditioning: what you need to know about its functioning  Inverter in air conditioner - what is it
Inverter in air conditioner - what is it  Dismantling the indoor unit for cleaning
Dismantling the indoor unit for cleaning  Replacing and checking the compressor and other parts of the air conditioner
Replacing and checking the compressor and other parts of the air conditioner 

