To heat a room in which one or more doors are constantly opening is an ungrateful task. The heaters operate at full power, but the heat still disappears through the doorways.
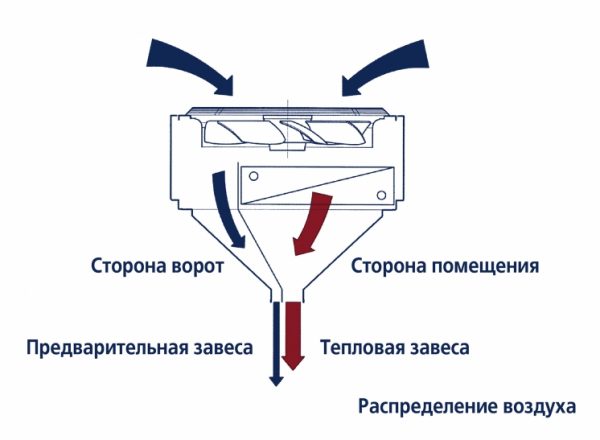
The optimal solution would be to establish a barrier in the opening, which allows people to pass through, but is an obstacle to the external flow of air. Such a device is called a thermal curtain, as it creates a flat stream of warm air in an open opening and does not allow the exit of warm masses to the outside and the entry of cold air inside.

Airflow protects doorway
The principle of operation of any thermal curtain
The task of such a protective device is to cut off the external air using the air itself. Namely - the creation of an insulating air flow that covers the entire open opening. Such a curtain not only retains heat indoors, but also prevents the penetration of dust, extraneous odors and even insects from the outside.
Air barrier
Such devices effectively retain heat where doors constantly open - in shops, garages. And in large country houses, situations may arise when the doors are constantly wide open.
Of course, the purchase of a thermal curtain costs money, and its work is accompanied by energy consumption. But the effect of heat preservation in a house protected by a curtain allows heating systems to work with less power. And this ultimately results in a total cost savings. In addition, modern devices of the thermal curtain are equipped with automation, which turns on the air barrier only with the door open, and when the door is closed, the curtain does not work and does not consume energy.
The device of the thermal curtain
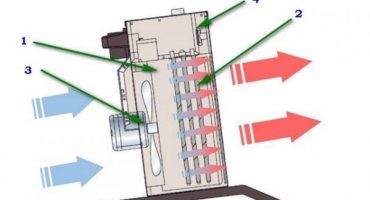
Simplified operation of the device that creates an air barrier can be represented as a combination of heating elements and a fan. Heated air is driven by a fan, and the outlet ducts and louvres form a wide and flat stream from it, directed along the protected space.
The simplified device of a thermal curtain
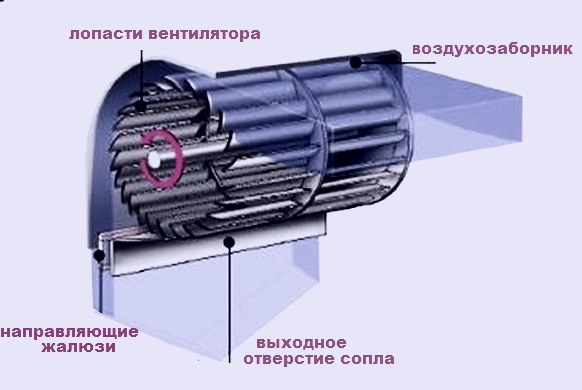
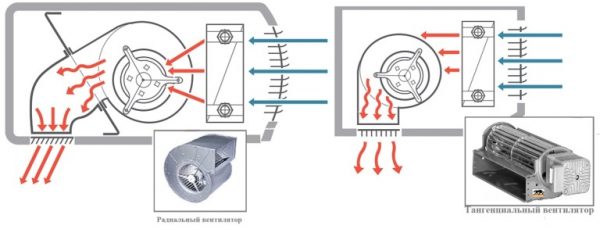
Of course, in fact, everything is not so simple. Conventional axial type fans are not suitable for creating a wide and uniform air flow. To ensure a high-quality air barrier, radial and diametrical fans are used. In shape it is a long cylinder, with blades along the entire length.
The scheme of operation of the thermal curtain
Typically, such a turbine is rotated by an electric motor located on the side. But there are options in which the engine is located in the middle and rotates two turbines on either side of itself. This design requires a sophisticated duct structure, since otherwise a narrow section is formed in the middle in which an air screen is not created.
The features of air protection devices vary by installation location, by type of heating elements and by control methods.
Installation location
The heat flux generated by the curtain can be directed from top to bottom or from the sides of the protected opening. Logically, the device that directs the air vertically should be called vertical. But according to a not entirely clear tradition, such veils are called horizontal. And those that drive air across doorways are vertical-type curtains.
Options for curtains at the installation location:
- Horizontal curtains are located above the opening, which must be "closed". The airflow is directed from top to bottom.This is the most common type of device. This is due to the fact that their installation is the easiest.
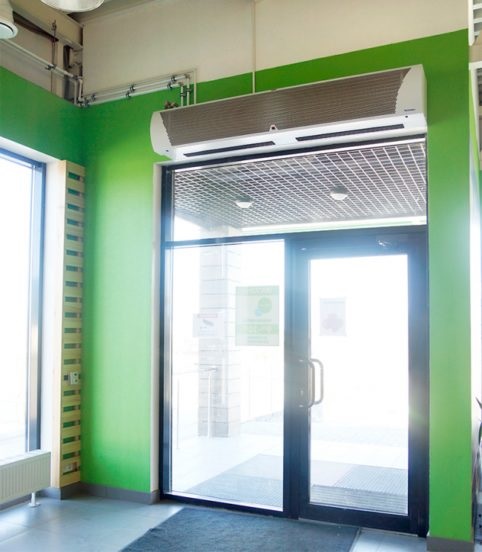

Horizontal type thermal curtain
- Vertical curtains are attached to the floor and are located on the side of the doorways. This arrangement is more difficult to manufacture the device itself and more difficult to install. What is a vertical thermal curtain for? You can not do without it in cases where there is not enough space above the door to install a horizontal device. In addition, for relatively narrow doors, the use of vertical type air protection may be more effective.
- There is another very rare type of thermal curtains - built-in. These devices are designed for covert installation behind a suspended ceiling. Airflow exits through the grill.
Types of heating elements
To ensure reliable protection of the room in cold weather, preliminary heating of the air is required before it is brought out. This is achieved by blowing heaters. The heating elements used in thermal curtain devices are of three types:
Electric
The most common type of heating element. Traditionally, these are heating elements - tubular electric heaters, in which heating is carried out by a nichrome spiral enclosed in an insulating tube. Such heaters are reliable and easy to operate.
Recently, an electric thermal curtain uses STICH elements to heat air. In them, heat generation also occurs when current flows through a nichrome wire or tape. The shape and location of the wire in these elements resembles needle radiators.
Thanks to this design, STIC elements instantly heat up, providing a high temperature of blowing air at the outlet. Their disadvantage is that due to the high temperature of the element itself, the dust falling on it burns out and a burning smell is released.
The relatively high cost of electricity also applies to the minuses of all electric heaters.
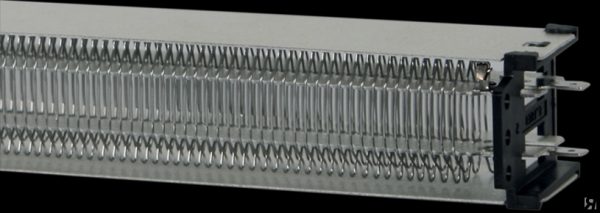
Heating STIC element
Water
These are water heaters that produce heat from the hot water passing through them. They are quite complicated during installation and operation.
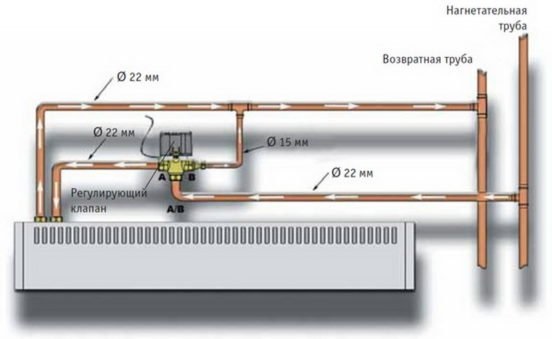
Water type heater for thermal curtain
Gas
Perhaps the most profitable in terms of cost. There are models that work on liquefied gas. The disadvantage is the possible danger of accidents inherent in any gas equipment.
Management methods
Monitoring and control of thermal protective devices can be carried out manually and automatically. Basic management methods:
- Turn on and off the device. Automation, synchronized with the opening of doors, provides cost savings and resource curtains. The protective flow is activated only with the doors open.
- Airflow temperature control. In simple devices, a manual temperature switch is used. In expensive devices, the degree of heating is regulated depending on the outdoor temperature. During hot weather, the heating elements can be switched off, and the curtain ensures the maintenance of coolness indoors.
- Remote control of operating modes is carried out using a portable remote control.
Specifications
To understand how to choose a suitable thermal curtain, you need to understand the main technical parameters of these devices. Choose the device that will protect your door:
- Sizes. The length of the device should provide full overlap of the width of the doorway with heat flow. Even a small gap will significantly impair the effectiveness of protection against external influences. To choose protection over wide doors in large rooms - supermarkets, car repair shops - you can install several devices located along the entire width of the opening. The height of the device also matters.If there is more free space above the protected opening, then you probably have to abandon the horizontal type of curtain and consider only options with a vertical type, with the location on the side of the doors.
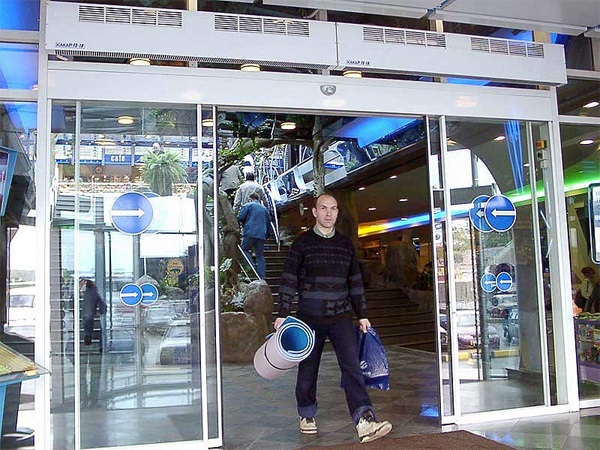

Creating a long four-element thermal curtain
- Air flow rate. The task of the thermal curtain is not heating the room - this role is played by other devices. Therefore, the fan power and, accordingly, the volume of air flow per unit time and its speed are the main parameters of the thermal curtain. A reliable setting of the protective flow requires its speed at a distant point of about 2 m / s. To ensure such a flow velocity near the floor, it is necessary that a device located at a height of 2.5 m "give out" a speed of the order of 8 m / s. To ensure such speeds, devices with a capacity of more than 600 m3 / hour are required.
- Noise level. If for industrial premises and large supermarkets this is not the most determining parameter, then for household devices it is critical. At home, less than 70 dB of noise is required for comfort.
- The presence of automation controls. Manual mode is only good for the simplest and cheapest options. Automatic control of the operation of the curtain and the temperature of its heating elements ensures its efficiency and economy.
- Protective devices. For security, the ability to automatically turn off the system when it overheats is necessary.
Popular models of thermal curtains
Consider the most popular models:
- One of the simplest, but at the same time powerful horizontal thermal shields is considered the Tropic M-9 model. Its purpose is production facilities, since it works from a 380 V network, and its design does not shine. Two power levels - 9 kW and 4.5 kW. High productivity - more than 1100 m3 / hour. Installation height - no more than 2.3 m. Price 12 - 13 thousand rubles.

Powerful curtain Tropic M-9
- For domestic use in homes and even apartments, Ballu BHC-L06-S03 can be a suitable model. It does not have much power, but low noise and low cost. It works from a 220 V network and also has two switchable power levels - 3 kW and 1.5 kW with heating from STICH elements. Possible operation with the heat turned off. Productivity - 350 m3 / hour. Noise level - 46 dB. Its price is 5 - 6 thousand rubles. The disadvantages include the lack of remote control.

Household thermal curtain Ballu BHC-L06-S03
- Domestic manufacturer Teplomash produces a whole line of thermal protective devices. One of the household models KEV-3P1153E. With a decent productivity - 500 m3 / hour, but low noise - 45 dB. Two-stage power adjustment - 3 and 1.5 kW. The maximum installation height is 2.2 m. The price is 6 - 7 thousand rubles.

Thermal veil Teplomash KEV-3P1153E
 Micathermic heater: pros and cons, what it is and how it works
Micathermic heater: pros and cons, what it is and how it works  Rating of infrared heaters - top-best models of 2018-2019
Rating of infrared heaters - top-best models of 2018-2019  Infrared heater or quartz - which is better
Infrared heater or quartz - which is better 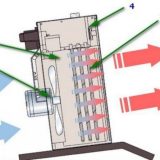 Fan heater or oil heater - which is better and more economical
Fan heater or oil heater - which is better and more economical  Heater or convector - which is better and what is the difference
Heater or convector - which is better and what is the difference