Boiler-type water heaters are designed to heat and maintain the temperature of large volumes of water. There are various methods of heating, but the use of electricity is considered the most efficient and affordable.
Among electric heating elements for more than a century, heating elements (tubular electric heaters) have been used. They are convenient and effective, so the name "TEN" has become famous and does not require additional explanation - and so it is clear what is being said. But recently, for heating elements used in water heating, additional clarification was required. A new type of heating elements has appeared, called “dry”. And the previous tubular heaters, respectively, began to be classified as “wet”. What is the difference?
Wet Heater Boilers
The classic heating element is a metal hermetic tube into which a heating coil, usually made of nichrome, is integrated. Heat-conducting filler is poured into the remaining space of the tube.
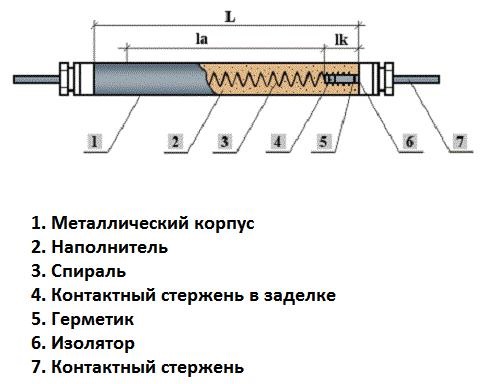
Conventional Tube Heater Device
The tube is built into a container in which water should be heated. Electric current heats the spiral, and then through the filler the heating is transferred to the walls of the tube, and from them to the water in the tank. The advantage of tubular heaters is that the tube can be bent as you like, giving it any shape.

Various forms of "wet" water heating elements
Such a variety of shapes allows you to embed the heater in different places of the heated tank - not only in the lower part, but also on the side and in inaccessible places. The heater is installed directly in the water tank through insulating gaskets. In the process, it is in direct contact with water. This gives its advantages in the form of rapid heating of water, but the constant presence in water adversely affects the operation of the heating element.
Despite the various shapes attached to the heating tubes, the mounting flanges of most heaters are standard. Therefore, there is often no need to look for exactly the same heater when replacing, another type of heater may be suitable.
Since the heating element is always in the water, it is called “wet”. But if there are wet heaters, then there must be dry ones.
"Dry" heater - design and features
The heating element of such a heater is also a nichrome spiral. But it is not inserted into the tube and insulated not with a filler, but with ceramic insulators.

The appearance of a dry heater
Separately, its elements look like this:

Separate elements of a “dry” heating element
From the figures it is clear that such a device cannot be immersed in water. It is not intended for contact with water, hence the name “dry”. The heater assembly is installed in a special flask made of metal or heat-conducting ceramic. The surface of metal flasks is coated with anti-corrosion enamel.

“Dry” heater in the flask
And the flask itself is built into the heated container and insulated with gaskets. Unlike the wet version, both the bulb and the heater itself are always made in a straight form, without any bends. And the “dry” heater is installed in the water heater only in the lower part of the tank.

Dry installation of a heater in a boiler
The fact that the heating element itself does not come into contact with the inner surface of the installation flask limits the rate of initial heating of water. And although the gaps between the heating element itself and the flask wall are minimal, nevertheless some time is spent on warming the air gap. For this reason, current dry-type constructions are not installed in instantaneous water heaters, and they are used only in storage water heating systems.
Comparison of wet and dry heaters
Despite the fact that “dry” heating elements are a more modern type of heating elements, boilers with “wet” elements are still produced by manufacturers and find their customers. Because even a modern element has its own drawbacks, and previous models are not without advantages.
Advantages and disadvantages of wet heaters
Advantages of “wet” heating elements:
- The initial heating rate. Heat from a nichrome spiral is quickly transferred to the water volume.
- Universality of models. To replace a failed heater, you can sometimes choose a heater of a different brand.
- Boilers with traditional wet heaters are cheaper.
Disadvantages of “wet” heaters:
- Relatively short life. The main reason is the formation of scale on the outer tube of the heater. As practice shows, most wet models fail after 5 years. And when using water with a chemical composition favorable for scale - even less. Scale corrodes the tube material and the heater fails.

Scale on the tubes of a "wet" heating element
- The second drawback is partially related to the first. If the “wet” heater has stopped working, then replacing it is not easy. Before replacing, be sure to drain the water from the boiler. For boilers with a non-standard arrangement of heaters, you need to remove the tank from the mounts. To seal when installing a new device, you will need a new gasket, as the old one will probably be damaged during dismantling.
- Scale not only destroys the heater body, but also hinders the heat exchange between it and water. Therefore, over time, the heating rate of the entire volume of water deteriorates, and the entire boiler consumes more electricity.
- Safety. If the heating element corroded by scale is not replaced in time, then there is a danger of electric shock.
Advantages of heating elements of the "dry" type
The main difference between “dry” and “wet” models is the lack of contact of the heating element with water. This leads to the fact that modern “dry” heaters last three times longer than traditional “wet” ones:
- Since the heating element is located in a flask isolated from water, no scale will form on it. He works in ordinary air, which positively affects the overall duration of his work. Heat transfer deterioration due to fouling also does not occur. Power consumption does not change over time.
If, nevertheless, the “dry” heater is out of order, then its replacement does not require special qualifications and is not fraught with any problems. For replacement, it is not necessary to drain the water from the boiler, and even more so, it will not be necessary to remove the tank itself from the mount. It is only necessary to unscrew the screws securing the heater to the insulating flask and remove the faulty element. The subsequent installation of the new element will not require insulating gaskets or sealants.
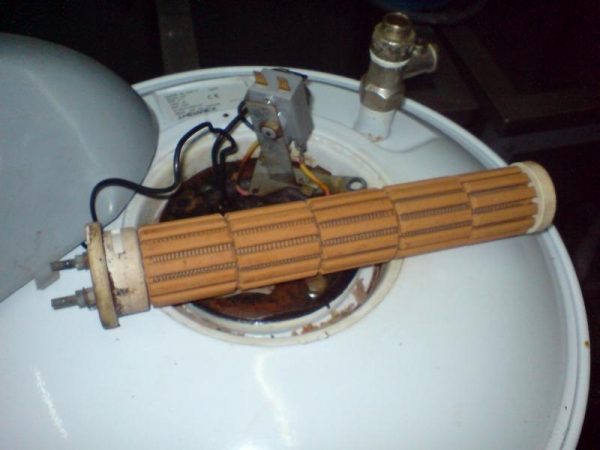

Dry heater removed from the bulb
- Increased electrical safety. Since contact of conductive parts with water is excluded, the risk of electric shock is minimal.
- Boilers with "dry" elements began to be released not so long ago. Therefore, all these models, as more modern, are equipped with special protective devices: protection against switching on in the absence of water; overheat protection; shutdown during electric breakdown of an element.
Disadvantages of dry type heaters
Even advanced technologies are not perfect. Originality and convenience of construction are accompanied by negative qualities:
- Prolonged initial heating due to the passage of heat from the heating element to the walls of the bulb. But for storage water heaters, this is not critical.
- Virtually no boilers up to 50 liters with "dry" elements are produced. Long straight elements are not suitable for small containers.
- The power of one “dry” heater does not exceed 1200 watts. But usually boilers are available with two elements that can work both separately and in pairs.
- Lack of universalization. Each “dry” element corresponds to a specific boiler model. Therefore, when replacing, you need to find exactly the same.
- Dry element water heaters are a bit more expensive.
Popular brands of dry heater boilers
The advantages of dry heating systems served as a signal for leading manufacturers of storage water heaters. The release of such models is no longer limited to single brands, but acquires a mass character.
A wide range of choices is provided by such companies: Swedish Electrolux, French Atlantic, Slovenian Gorenje.
Here are some models of dry storage boilers from these manufacturers:
| Manufacturer | Model | Tank volume, liter | Power consumption | Additional functions | Estimated cost, rub. |
| Atlantic | Steatite Slim VM 80 N3 CM | 80 | 2100 | Overheat protection, safety valve | 12 000 |
| Atlantic | Cube Steatite 150 S4CM | 150 | 2400 (1200 + 1200) | Overheat protection, safety valve | 22 000 |
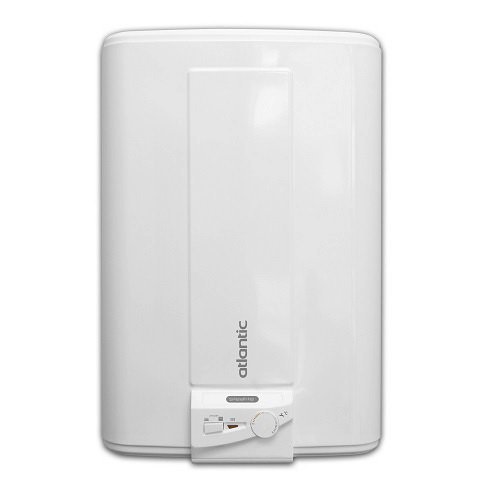

Boiler Atlantic Cube Steatite 150 S4CM
| Manufacturer | Model | Tank volume, liter | Power consumption | Additional functions | Estimated cost, rub. |
| Electrolux | EWH 80 Formax DL | 80 | 2000 (800 + 1200) | Overheat protection, display indication | 16 000 |
| Electrolux | EWH 100 Formax DL | 100 | 2000 (800 + 1200) | Overheat protection, electronic control | 20 000 |
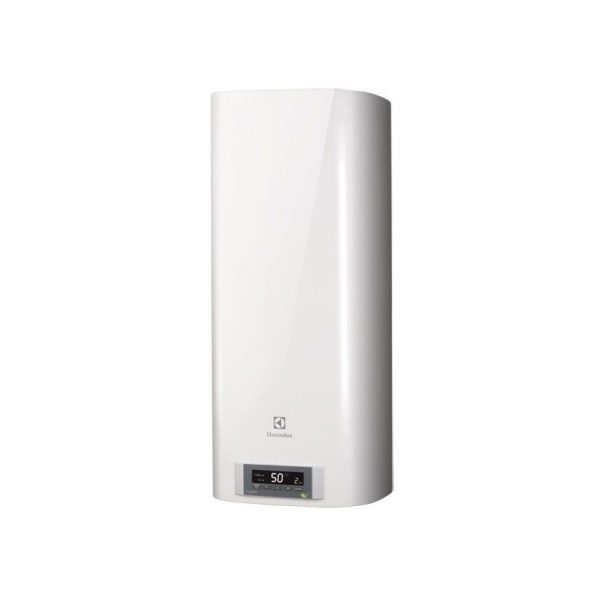

Boiler Electrolux EWH 80 Formax DL
| Manufacturer | Model | Tank volume, liter | Power consumption | Additional functions | approximate cost |
| Gorenje | OGBS80ORV9 | 80 | 2000 (1000 + 1000) | Frost protection; safety valve | 11 000 |
| Gorenje | GBFU 150 B6 | 150 | 2000 (1000 + 1000) | Frost protection | 15 000 |

Boiler Gorenje GBFU 150 B6
Summing up, we can say that in the near future, boilers with “wet” and “dry” heating elements will develop and improve, complementing and adopting each other's qualities. But the “dry” type looks more promising. A breakthrough may occur when “dry” heaters can work in flow systems.
 What is a instantaneous water heater, how does it work and how to use it
What is a instantaneous water heater, how does it work and how to use it  How to properly drain water from a water heater
How to properly drain water from a water heater  Set the temperature of the water heater and determine by the strip
Set the temperature of the water heater and determine by the strip  Do-it-yourself dismantling of the water heater and individual parts
Do-it-yourself dismantling of the water heater and individual parts  Installation and connection of instantaneous water heater - step by step instructions
Installation and connection of instantaneous water heater - step by step instructions 

