For a person accustomed to comfort, the lack of hot water, even for several hours, seems like a disaster. A huge variety of household heating devices, together with an affordable price, make the purchase and installation of appliances an easy way to solve the problem of hot water supply. However, during installation, inexperienced users, by negligence or ignorance, “forget” to make the grounding of the water heater.

Storage water heaters - boilers
What the violation of the rules for connecting to the mains, the lack of grounding, and how to properly protect yourself from electric shock do it yourself, is described in the article.
Why ground the water heater
Water entering the water supply system is a good conductor, and electric heaters in apartments and private houses are powered by electricity. Regardless of the type of electrical appliance (flowing or storage), the liquid is in contact with the heating element.
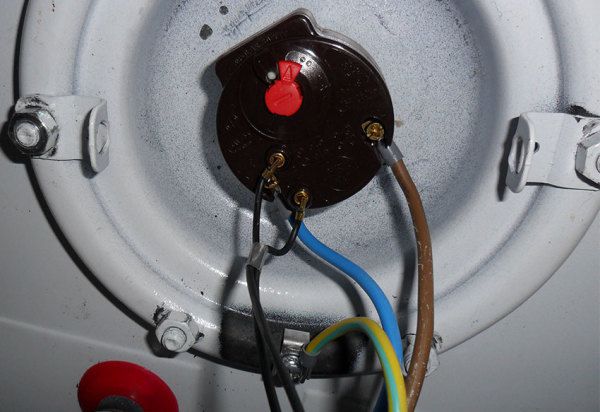
The contact group of the boiler is a yellow-green wire for grounding the housing
In the case of burning off the conductors, destruction of the heater body, contact of the phase housing on the body, contact between water and the bare wire cannot be avoided. The fluid becomes a conductor for leakage current. In cases where the user touches the ungrounded metal casing of the device or substitutes parts of the body for a stream of water, electric current will flow along the path: phase 220 V - water heater - human body - earth (through water). A tangible blow, often leading to fatal cases, is inevitable.
In another case, a potential difference may arise between two electrical appliances (often the not quite correct name “stray currents” can be found) located in the same room. In this case, the simultaneous touch of the devices also leads to tangible “tingling”. Grounding in such cases serves to equalize the potentials of the circuits. In addition, the presence of "extra" potentials on devices accelerates their destruction.
Grounding methods and principles
There are two different ways to protect against electric shock - protective grounding and grounding. Out of ignorance, authors often call them grounding in one word.
What is the difference? In the case of "real" grounding, the metal case of the electrical appliance is connected by a separate conductor to a special circuit. How to make it in a private house or in the country we will tell below.
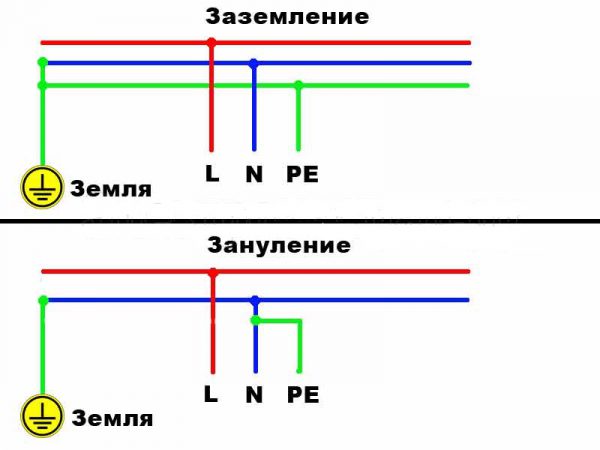
Block diagrams of grounding and grounding
In this case, the operating voltage that has arrived at the device is discharged along the path: electrical installation enclosure - conductor - ground bus - earth. The resistance of such a circuit according to the rules of the electrical installation should not exceed 4 OM, which is much less than the resistance of human skin. Thus, all the current will go to earth. If the amperage is large, then the circuit breaker will work - the power supply to the consumer's electrical installation (as electrical appliances are correctly called) will be turned off.
In case of grounding, an additional wire is present in the outlet (painted yellow-green) and is called a PE conductor. The ground wire in the heater is connected to hazardous parts of the appliance that could become a source of current leakage.In case of violation of the integrity of the heating element, if the phase enters the housing, the current will flow along the path: phase wire - device housing (heater) - protective earth wire - distribution panel of the apartment. If the rated current is exceeded, the protection device will trip.
The choice of the type of grounding of any type of water heaters in the apartment depends on the organized power supply scheme of the apartment building.
How not to ground electrical appliances
There are several simple, at first glance, ways to organize protection in your apartment, but it is strictly forbidden to use it:
- The connection of the third wire in the outlet with water pipes or heating pipes passing through the kitchen or in the bathroom.

Prohibited grounding on a water pipe
- In the event of a phase breakdown on the heater or washing machine body, all the dangerous potential will fall on the riser. The neighbor who discovered the water is doomed to electric shock. Moreover, this method does not work in case of replacing part of the metal pipes with plastic analogues - the "grounding" will not fulfill its function.
- Union in the socket of the zero and grounding contacts. A zero break in such cases leads to the appearance of dangerous voltage on the buildings of all consumers connected to the network of the apartment.
- Grounding several devices in series with each other. If a malfunction occurs in one device, all the others will be under dangerous voltage.
- Connection of several wires to one bus terminal. Each device must have a separate contact.
- Self-fabrication of grounding devices and connecting busbars to them. Such devices can disrupt the operation of the entire power supply system at home and not fulfill their purpose at all.
Wiring diagram of an apartment building
Until 1998, according to the then current regulations, most of the houses were powered by the so-called TN-C circuit or a circuit with dead-grounded neutral.
A four-core cable was supplied in the house, in which there were 3 phases and one neutral conductor. In an apartment, such a system is easy to identify - all outlets do not have a protective contact, they are two-contact.
In modern buildings, power is supplied by a five-core cable (TN-S wiring), in which the working and protective neutral wires are separated. Sockets have a protective contact, as well as when using the TN-C-S circuit. There are other grounding schemes.
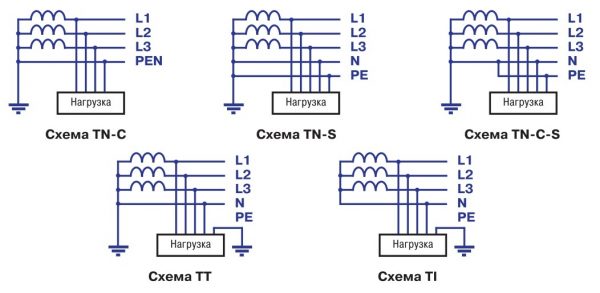
Grounding schemes
“The figure shows the possible options for the organization of power supply and grounding. If there is no exact information about which scheme is organized in your home, contact the energy company of the management company. ”
How to ground a water heater in an old house
In the houses of the old building for the organization of grounding, you will have to perform a number of works and spend money on the purchase of materials.
A single-core copper wire with a cross section of at least 4 mm is purchased2, which, on the one hand, is connected to the grounding terminal on the appliance. The other end of the wire is attached to the busbar in the floor panel. It is advisable to lay the wire in the gate to prevent damage. To connect to the ends of the wire, solder the contact for tightening under the bolt.
Use of RCD
Another way to protect yourself from electric shock is to install a residual current device (RCD) or differential circuit breaker.
The device is placed separately on the water heater or on the general input of the wiring.
The essence of the operation of devices, in short, is as follows. The device is installed in the gap of both conductors (phase and zero), through which the premises are powered. Under normal operating conditions, the currents flowing through the phase and neutral conductor are equal. The power remains connected.
If a leakage current occurs through one of the wires, the values of the flowing currents will become different. A residual current device or differential circuit breaker will disconnect both conductors from the consumer.
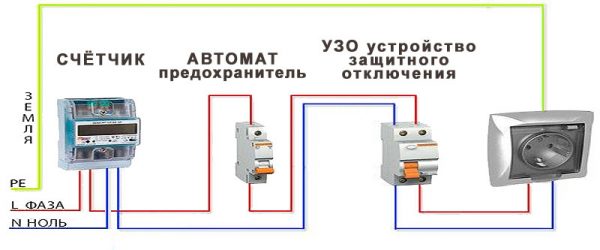
RCD circuit
For installation in residential premises, it is provided for the installation of such disconnection devices that respond to a leakage current of 30 mA. The response time of devices does not allow to receive an electric shock hazardous to health.
What to do in private homes
Arrange an individual grounding system in a private house or in a summer cottage for any property owner.
Important! If there is not enough special knowledge, we strongly recommend that you contact an electrician specialist in the village management company (the board of the summer house). This will help to avoid mistakes during construction work and when connecting.
In any case, it is better to complete the general construction part on your own - this will save a significant amount of money.

The construction part of the manufacture of individual grounding
Production Order:
- Having departed from the foundation of the house, 1.5 - 2 meters dig a trench in the shape of an equilateral triangle with a side of 2 - 2.5 m. The depth of the recess is 60 cm, the width is 40 - 50 cm. A recess is also digged between the triangle and the wall of the house for connecting the bus to the distribution visor.
- At the corners of the triangle, pins of metal reinforcement 12-14 mm in diameter are driven into the ground, leaving 5-10 cm above the bottom of the trench.
- Hammered pins are interconnected, welding a metal strip with a thickness of 4 mm and a width of 40 mm. The same strip, welded to the pins, is displayed on the wall of the building.
- They dig the trench.
- Bolts with a thread diameter of 8-10 mm are welded to the strip brought to the wall - ground wires from household electrical appliances (boilers, washing machines and dishwashers, various machines) will be connected to them.
- Heater ground terminal with a 4 mm single-core copper wire2 or aluminum section 6 mm2 connect with a bolt welded onto the tire. Connection is carried out "under the bolt."
So, the connection of domestic water heaters and other energy-intensive devices to the protective grounding system is caused by the need to comply with safety regulations.
The device saves the lives of users in the event of malfunctions of electrical appliances and minimizes the likelihood of fires. A simple grounding system will help to avoid tragedies when using electrical appliances.
 What is a instantaneous water heater, how does it work and how to use it
What is a instantaneous water heater, how does it work and how to use it  How to properly drain water from a water heater
How to properly drain water from a water heater  Set the temperature of the water heater and determine by the strip
Set the temperature of the water heater and determine by the strip 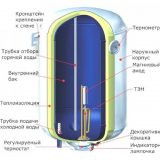 Do-it-yourself dismantling of the water heater and individual parts
Do-it-yourself dismantling of the water heater and individual parts  Installation and connection of instantaneous water heater - step by step instructions
Installation and connection of instantaneous water heater - step by step instructions 

