To choose a good binocular, you need to know the basic principles of its operation, the design features of various systems, their advantages and disadvantages. It is important to consider why the device is planned to be used: observation, hunting, studying the starry sky, etc., since different types of devices are produced for different purposes. Only then can one proceed to the choice. The article aims to help readers choose the best binoculars for their goals.
| Category | Title | price, rub. | Short description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rating of the best binoculars of 2019 | Nikon Aculon A211 10 × 50 | 6999 | An excellent choice as a universal field binocular. Optimum price-quality ratio. |
| Nikon Aculon A211 8 × 42 | 5890 | One of the best for daytime use. | |
| Yukon Sideview 10 × 21 | 3314 | The best binoculars for hunting, presented in the ranking, in terms of price and quality. | |
| Olympus 8-16 × 40 Zoom DPS I | 6790 | For long daytime stationary observations, which require a shift increase. | |
| Celestron SkyMaster 15 × 70 | 8290 | A good astronomical device with a low price. | |
| Olympus 8 × 40 DPS I | 5999 | An excellent device for evening observation. | |
| Celestron UpClose G2 16 × 32 Roof | 2990 | Good for use on mountain hikes. | |
| Nikon Action EX 7 × 35 CF | 10490 | Ideal for stationary observations in adverse weather conditions, in water. | |
| Canon 10x42L IS WP | 14990 | Good for long observations on the sea or on the river. | |
| Yukon Expert VMR 8 × 40 | 11495 | Thanks to various filters it is suitable for observation in the evening under bad weather conditions. |
General characteristics
Binoculars, in fact, are two visual parallel mounted tubes. Its advantage is compactness and the ability to observe distant objects with two eyes.
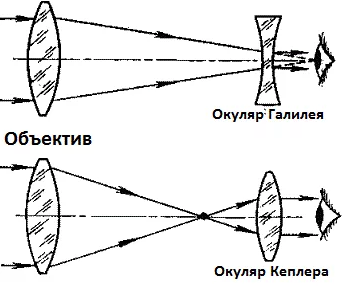
Optical systems of Galileo and Kepler are used in binoculars:
- Galilee consists of a lens - a positive lens and an eyepiece, which is a negative lens. Disadvantages: due to the laws of optics, the viewing angle is small. With a multiplicity greater than 4, the picture quality deteriorates. Such models do not fall into any binoculars rating, since they are in very limited demand. The article will not be considered.
- In the Kepler system, the lens and eyepiece are positive lenses. Thanks to this, a wide viewing angle and a large aperture are achieved. The image is turned upside down. A distinctive feature of the Keplerian scheme is a large focal length, which lengthens the design. To reduce the design, as well as to wrap the image, optical prisms are used in the Kepler system.
Lens and eyepiece
Both the eyepiece and the lens are collecting lenses. One of the main characteristics of such a lens is its focal length. This is the distance from the plane of the collecting lens to the point (main focus) at which the rays of light refracted by it converge.
Focal length ratios: Г = Fоб / Фок, where Г - increase, Фоб - focal length of the lens, Fok - focal length of the eyepiece. The more Fob and less Fok, the stronger the device brings the image closer. For example, if the focal length of the lens is 400 mm, the eyepiece is 20 mm, they provide a 20-fold increase.
The next important characteristic is the diameter of the lens (aperture). The amount of incident light in the eye of the observer is in direct proportion to this value. Optical systems that collect light well are good for use at dusk and for astronomical observations.
When dividing the aperture by the multiplicity, the numerical value of another indicator is obtained - the exit pupil. For comfortable use, it is necessary that it is less than or equal to the diameter of the pupil of the eye: about 5 mm.
Attention! For the eyepiece, the most important indicator is the removal of the exit pupil. This is such a distance from the surface of the eyepiece lens where the pupil of the observer should be placed to achieve the maximum field of view. The comfortable value is 10-15 mm.
Modern lenses and eyepieces have a complex structure consisting of several connected lenses. Thanks to this, it is possible to significantly reduce the geometric and chromatic distortion of the image. Lenses are made of special optical glass. A brightening coating is applied to them, which reduces the absorption of light.
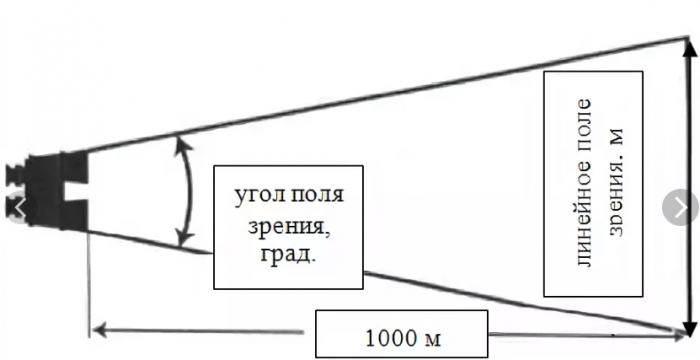
Field of view
This is a region of space visible in the visual device and measured in angular quantities (degrees, minutes). The name "viewing angle" is found. It is connected with a linear field of view by an optical system, which shows the minimum size (in meters) of objects visible from a distance of 1000 meters. The larger the viewing angle, the greater part of the space can be observed.
If the visual device has a large viewing angle, it is more convenient to observe into it: it covers more space, it is easier to notice fast-moving objects. The price of such models is higher than standard.
Prismatic
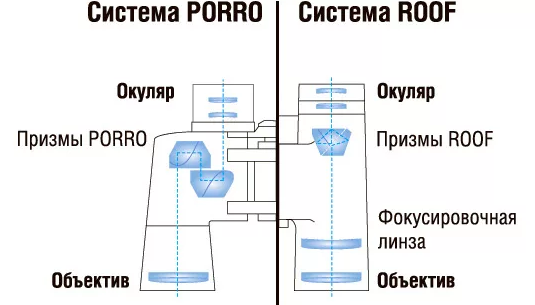
An optical device with a large focal length has significant dimensions. To reduce the size, as well as wrapping the image, prism blocks are used.
In modern models, blocks of prisms of two types are used: Porro, so named after the author, Ignazio Porro, and ruf (Eng. Roof - roof) or prisms of Abbe - König.
In the Porro system, two prisms of the same shape are installed next to each other. Binoculars with the Porro system have a characteristic yielding appearance, due to the fact that the distance between the optical axes of the lenses is greater than the distance between the axes of the eyepieces.
In Ruf's, prisms have a different shape and are connected in a block resembling a gable roof (hence the name). The main difference from the previous system: the optical axis of the lenses and eyepieces almost coincide. Thanks to this, compactness and lightness of construction are achieved. However, due to such a scheme, lenses with a diameter greater than 60 mm cannot be used, since in this case the distance between the optical axes of the eyepieces is greater than the distance between the pupils of the eyes.
Due to the complex design of the prism block, the use of special varieties of optical glass, special antireflection and phase-correcting coatings, the price of a model with a ruf system is one and a half times higher than that comparable with the main characteristics of the device with a porro system.
Housing
Protects optical components from mechanical damage. Production material - polycarbonate or magnesium alloys, which have lightness and strength. Which is better - difficult to answer. Each has its pros and cons. Definitely worth avoiding products made of cheap plastics.
Binocular housings designed for adverse weather conditions are protected against moisture. Fully sealed models are available that can withstand immersion in water at a 5-meter depth. The sealed housing allows drained nitrogen to be pumped inside. It prevents fogging of the lenses of the eyepiece and lens from the inside during sudden changes in temperature. Additional protection provides a rubberized coating with anti-slip effect.
Types of binoculars
The following types of binoculars are available:
- Field (for the field observer). It is used to review large open areas in all weather conditions in the morning, afternoon and evening, therefore it is characterized by increased aperture. It is considered optimal if the optical magnifies the image 7-10 times, and its aperture is 40 - 50 mm. The construction is mainly made using Porro prisms. Such models are always at the top of sales.
- Military (army). Optical characteristics are similar to the previous view. It has increased strength, water resistance. Weight less than 700 grams due to lightweight magnesium alloys. Equipped with a rangefinder grid. Visual equipment has appeared in the armed forces that performs several functions: monitoring at any time of the day (built-in thermal imager), measuring the distance to objects with an integrated laser range finder, providing target designation, etc.But these are, rather, information-observational complexes having an indirect relation to classical optical instruments.
- Astronomical. Amateur astronomers often wonder how to choose a good binocular with high magnification. This device is just for them. It has a very large aperture (up to 100 mm), a wide viewing angle and a significant magnification (up to 25x). Since the mass reaches 4 kg, it is used only with a tripod. It can be considered as a kind of telescope, therefore, for example, it is often used by amateur astronomers to search for weak comets.
- Nautical. Designed to work in the most severe climatic conditions. Some models allow full immersion in water for up to 5 minutes. Weight reaches 1 kg. An antireflection coating resistant to the action of sea water that withstands an aggressive marine environment is applied to the lenses. Magnification 10-15x. There are models with a built-in stabilizer to compensate for the effect of pitching. It can also be equipped with a built-in compass.
- For hunting. General requirements: weight up to 400 g, wide viewing angle, magnification 7-10x. No need to constantly monitor the surrounding space. A light, reliable, ready-to-use device at any moment is needed, most of the time in a case. Therefore, the best binoculars designed for hunting are available with a roof system. It provides the necessary compactness and lightness of the product. Additional requirements: aperture 25-40 mm, rubberized coating.
- Night vision. In low light conditions, two types of devices are used: with an electron-optical converter and an infrared matrix. The former enhance the brightness of the image using the light of stars and the moon. The second, capturing the thermal radiation of surrounding objects, build on its basis a human-visible image. Both systems are not optical in the full sense of the word, since they require additional power sources and electronic systems for imaging to work. Such systems are often additionally equipped with laser rangefinders, memory cards for recording the resulting image. They are used for night observation and hunting.
- Variable multiplicity. It is often presented by manufacturers as a universal model for any conditions. Especially emphasizes the maximum multiplicity (up to 100x). This is achieved by a significant complication of the design. It is impossible to ensure absolutely synchronous operation of variable multiplicity mechanisms in each pipe. In addition, a complex optical design reduces the viewing angle. Therefore, it can be recommended only to those observers to whom a quick change in the multiplicity can help in the work, for example, ornithologists during the study of birds in bird markets, etc.
Rating of the best binoculars of 2019
The proposed rating of the best binoculars for the spring of 2019 includes the models that are most popular with buyers. The aperture (diameter of the lens), the size of the exit pupil, are given in millimeters, the field of vision (per 1000 m) is in meters, weight is in grams.
Nikon Aculon A211 10 × 50
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 10x;
- aperture 50;
- exit pupil: 5;
- field of view: 114;
- weight: 900;
- average price: 6999 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: a great choice as a universal field binoculars. Optimum price-quality ratio.
Nikon Aculon A211 8 × 42
Characteristics:
- magnification: 8x;
- lens diameter: 42;
- exit pupil: 5.3;
- field of view: 140;
- weight: 755;
- average price: 5890 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: one of the best for use in the daytime.
Yukon Sideview 10 × 21
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 10x;
- aperture: 21;
- exit pupil: 2.1;
- weight: 199;
- average price: 3314 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: perhaps the best binoculars for hunting, presented in the ranking, in terms of price and quality. Good for long-distance hiking.
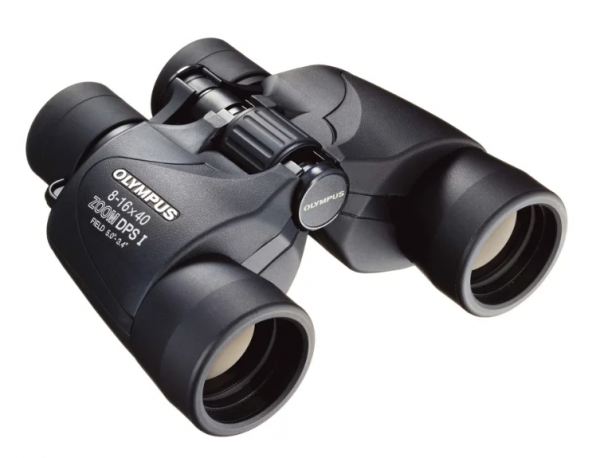
Olympus 8-16 × 40 Zoom DPS I
Characteristics:
- magnification: 8-16x
- aperture: 40;
- exit pupil: 3.4-5;
- field of view: 59-87;
- weight: 790;
- average price: 6790 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: for long daytime stationary observations, which require a shift increase.
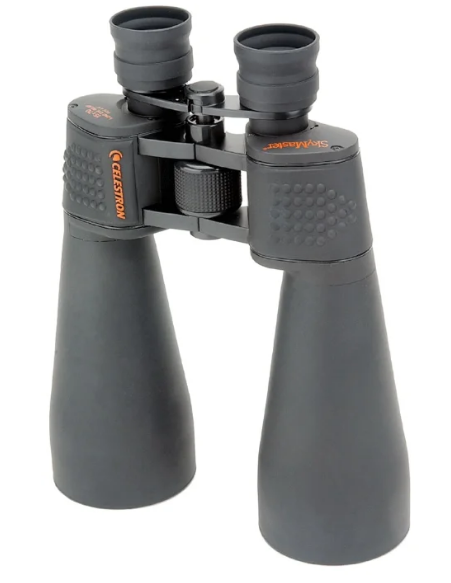
Celestron SkyMaster 15 × 70
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 15x;
- aperture: 70;
- exit pupil: 4.7;
- mass: 1360;
- average price: 8290 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: a good astronomical device with a low price. It requires a careful attitude, therefore it should be applied strictly for its intended purpose.
Olympus 8 × 40 DPS I
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 8x;
- aperture: 40;
- exit pupil: 5;
- field of view: 143;
- weight: 710;
- average price: 5999 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: an excellent device for evening observations.
Celestron UpClose G2 16 × 32 Roof
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 16x;
- aperture: 32;
- exit pupil: 2;
- field of view: 62;
- case material: metal;
- weight: 369 g;
- average price: 2990 r.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: good for use in mountain hikes, like binoculars for hunting in the steppe, for daytime observations of distant objects in a wide area.
Nikon Action EX 7 × 35 CF
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 7x;
- aperture: 35;
- exit pupil: 5;
- field of view: 163;
- inert gas filling: yes;
- weight: 800;
- average price: 10490 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Ideal for stationary observations in adverse weather conditions, in water.
Canon 10x42L IS WP
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 10x;
- aperture: 42;
- exit pupil: 4.2;
- field of view: 114;
- weight: 1030;
- average price: 14990 r.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: good for long-term observations at sea or on the river.
Yukon Expert VMR 8 × 40
Main characteristics:
- magnification: 8x;
- aperture: 40;
- exit pupil: 5;
- field of view: 126;
- inert gas filling: yes;
- weight: 800;
- average price: 11495 p.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion: due to various filters it is suitable for observation in the evening under bad weather conditions, during fog and snowfall.








 SLR camera
SLR camera  Nikon canon
Nikon canon  Top 5 best off-road electric scooters
Top 5 best off-road electric scooters  TOP-5 electric meat grinder 2020
TOP-5 electric meat grinder 2020  12 best electric toothbrushes
12 best electric toothbrushes 

